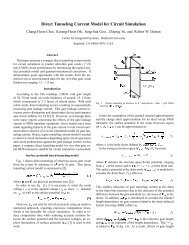
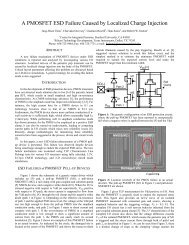
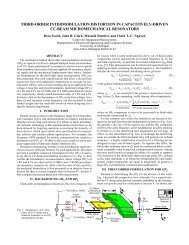
characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
56 Chapter 3. Simulation: Methods <strong>and</strong> Applications<br />
One <strong>of</strong> the most powerful features <strong>of</strong> device simulation is the ability to examine at any<br />
location in the device properties such as temperature, potential, <strong>and</strong> current density which<br />
are not accessible through real measurements. However, the huge quantity <strong>of</strong> available<br />
information is also a drawback because simple results must be extracted from the complex<br />
device-simulation models. Although extracting points from a MOSFET snapback I-V<br />
curve is straightforward, extraction <strong>of</strong> a parameter such as the time to failure for a given<br />
input power is nontrivial because “failure” is not directly defined in simulation. Instead, it<br />
must be determined using some criteria involving the parameters available in the<br />
simulation, such as temperature, J ⋅<br />
E pr<strong>of</strong>iles, <strong>and</strong> sudden drops in device voltage.<br />
Interpretation <strong>of</strong> simulation results is therefore just as important as accurately defining the<br />
models. In a way this is the converse <strong>of</strong> ESD testing, in which a simple leakage<br />
measurement determines whether a circuit has failed but the source <strong>of</strong> the failure cannot<br />
be ascertained without extensive testing <strong>and</strong> failure analysis.<br />
There are <strong>of</strong> course limitations to the application <strong>of</strong> 2D device simulation to studying ESD<br />
<strong>circuits</strong>. The accuracy <strong>of</strong> <strong>modeling</strong> thermal failure is one <strong>of</strong> the biggest concerns because<br />
there is no way to account for heat dissipation in the third dimension, which becomes<br />
important for long stress times. Section 3.6 discusses the implications <strong>of</strong> 2D <strong>modeling</strong> on<br />
predicting thermal failure. Two-dimensional simulation is also unable to examine edges<br />
<strong>and</strong> corners <strong>of</strong> devices or to study the susceptibility <strong>of</strong> semiconductor-metal <strong>and</strong> metalmetal<br />
contacts <strong>and</strong> interconnects. Mixed-mode simulations can be used to model the<br />
separate MOSFET devices <strong>of</strong> a multiple-finger circuit, but there is no way to model the<br />
flow <strong>of</strong> heat between the closely spaced fingers. For these reasons, the focus <strong>of</strong> the<br />
simulations is on individual devices <strong>of</strong> an ESD <strong>protection</strong> circuit, particularly MOSFETs.<br />
The following sections present physical models <strong>and</strong> general simulation techniques which<br />
facilitate ESD device simulation <strong>and</strong> then discuss specific ways in which the models <strong>and</strong><br />
techniques can be applied. First is a discussion <strong>of</strong> the facets <strong>of</strong> simulation which make<br />
studying ESD possible: implementation <strong>of</strong> the thermal diffusion equation, temperaturedependent<br />
mobility <strong>and</strong> impact-ionization models, curve tracing, <strong>and</strong> mixed-mode<br />
simulation. This is followed by a review <strong>of</strong> published studies on the application <strong>of</strong> 2D<br />
device simulation to ESD. Methods used to model the MOSFET I-V curve, thermal<br />
failure, dielectric failure, <strong>and</strong> latent damage are then discussed.