2294 part 1 final report.pdf - Agra CEAS Consulting
2294 part 1 final report.pdf - Agra CEAS Consulting
2294 part 1 final report.pdf - Agra CEAS Consulting
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Prevention and control of animal diseases worldwide<br />
Part I: Economic analysis: prevention versus outbreak costs<br />
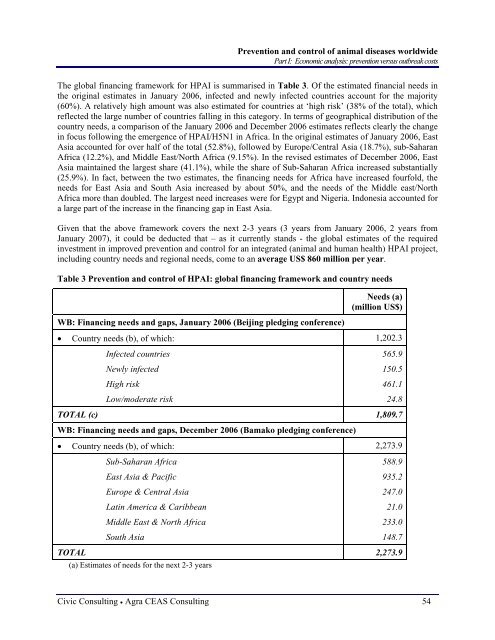
The global financing framework for HPAI is summarised in Table 3. Of the estimated financial needs in<br />
the original estimates in January 2006, infected and newly infected countries account for the majority<br />
(60%). A relatively high amount was also estimated for countries at ‘high risk’ (38% of the total), which<br />
reflected the large number of countries falling in this category. In terms of geographical distribution of the<br />
country needs, a comparison of the January 2006 and December 2006 estimates reflects clearly the change<br />
in focus following the emergence of HPAI/H5N1 in Africa. In the original estimates of January 2006, East<br />
Asia accounted for over half of the total (52.8%), followed by Europe/Central Asia (18.7%), sub-Saharan<br />
Africa (12.2%), and Middle East/North Africa (9.15%). In the revised estimates of December 2006, East<br />
Asia maintained the largest share (41.1%), while the share of Sub-Saharan Africa increased substantially<br />
(25.9%). In fact, between the two estimates, the financing needs for Africa have increased fourfold, the<br />
needs for East Asia and South Asia increased by about 50%, and the needs of the Middle east/North<br />
Africa more than doubled. The largest need increases were for Egypt and Nigeria. Indonesia accounted for<br />
a large <strong>part</strong> of the increase in the financing gap in East Asia.<br />
Given that the above framework covers the next 2-3 years (3 years from January 2006, 2 years from<br />
January 2007), it could be deducted that – as it currently stands - the global estimates of the required<br />
investment in improved prevention and control for an integrated (animal and human health) HPAI project,<br />
including country needs and regional needs, come to an average US$ 860 million per year.<br />
Table 3 Prevention and control of HPAI: global financing framework and country needs<br />
Needs (a)<br />
(million US$)<br />
WB: Financing needs and gaps, January 2006 (Beijing pledging conference)<br />
• Country needs (b), of which: 1,202.3<br />
Infected countries<br />
Newly infected<br />
High risk<br />
Low/moderate risk<br />
565.9<br />
150.5<br />
461.1<br />
24.8<br />
TOTAL (c) 1,809.7<br />
WB: Financing needs and gaps, December 2006 (Bamako pledging conference)<br />
• Country needs (b), of which: 2,273.9<br />
Sub-Saharan Africa<br />
East Asia & Pacific<br />
Europe & Central Asia<br />
Latin America & Caribbean<br />
Middle East & North Africa<br />
South Asia<br />
588.9<br />
935.2<br />
247.0<br />
21.0<br />
233.0<br />
148.7<br />
TOTAL 2,273.9<br />
(a) Estimates of needs for the next 2-3 years<br />
Civic <strong>Consulting</strong> • <strong>Agra</strong> <strong>CEAS</strong> <strong>Consulting</strong> 54