Chapter 10 Memory Subsystem.pdf
Chapter 10 Memory Subsystem.pdf
Chapter 10 Memory Subsystem.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
GPMC_FCLK<br />
GPMC_CLK<br />
gpmc_a[11:1]<br />
(connected to A[9:0] on<br />
memory side)<br />
gpmc_d[15:0]<br />
(connected to D[15:0] on<br />
memory side)<br />
nBE1/nBE0<br />
nCS<br />
nADV<br />
nOE<br />
WAIT<br />
CSRDOFFTIME<br />
CSONTIME<br />
ADVRDOFFTIME<br />
ADVONTIME<br />
OEOFFTIME<br />
OEONTIME<br />
RDCYCLETIME<br />
RDACCESSTIME<br />
Public Version<br />
www.ti.com General-Purpose <strong>Memory</strong> Controller<br />
<strong>10</strong>.1.5.7 WRITE PROTECT (nWP)<br />
When connected to the attached memory device, the WRITE PROTECT signal can enable or disable the<br />
lockdown function of the attached memory.<br />
The gpmc_nwp output pin value is controlled through the GPMC.GPMC_CONFIG[4] WRITEPROTECT bit,<br />
which is common to all CS.<br />
<strong>10</strong>.1.5.8 BYTE ENABLE (nBE1/nBE0)<br />
BYTE ENABLE signals (nBE1/nBE0) are:<br />
• Valid (asserted or nonasserted according to the incoming system request) from access start to access<br />
completion for asynchronous and synchronous single accesses<br />
• Asserted low from access start to access completion for asynchronous and synchronous multiple read<br />
accesses<br />
• Valid (asserted or nonasserted, according to the incoming system request) synchronously to each<br />
written data for synchronous multiple write accesses<br />
<strong>10</strong>.1.5.9 Asynchronous Access Description<br />
In asynchronous operations:<br />
• GPMC_CLK is not provided outside the GPMC.<br />
• GPMC_CLK is kept low.<br />
<strong>10</strong>.1.5.9.1 Asynchronous Single Read<br />
<strong>10</strong>.1.5.9.1.1 Asynchronous Single Read Operation on a Nonmultiplexed Device<br />
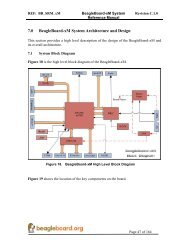
Figure <strong>10</strong>-<strong>10</strong> shows an asynchronous single read operation on a nonmultiplexed device.<br />
Figure <strong>10</strong>-<strong>10</strong>. Asynchronous Single Read on an Address/Data-Nonmultiplexed Device<br />
Valid Address<br />
Data 0 Data 0<br />
SPRUGN4L–May 20<strong>10</strong>–Revised June 2011 <strong>Memory</strong> <strong>Subsystem</strong><br />
Copyright © 20<strong>10</strong>–2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated<br />
gpmc-0<strong>10</strong><br />
2123