LINEAR ALKYLBENZENE SULFONATE (LAS) - UNEP Chemicals
LINEAR ALKYLBENZENE SULFONATE (LAS) - UNEP Chemicals
LINEAR ALKYLBENZENE SULFONATE (LAS) - UNEP Chemicals
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
OECD SIDS <strong>LINEAR</strong> <strong>ALKYLBENZENE</strong> <strong>SULFONATE</strong> (<strong>LAS</strong>)<br />
Method: Tests were conducted as an aqueous fraction in the presence of sediment.<br />
Natural stream sediments (71% clay, 19% fine silt, 4% medium sand, 6%<br />
fine sand) were collected from a pristine site in Rapid Creek, SD. Before<br />
testing, wet sediment was autoclaved for 40-60 minutes to reduce microbial<br />
populations and minimize initial rates of surfactant biodegradation. <strong>LAS</strong> was<br />
added to a sediment slurry at a nominal concentration and stirred overnight,<br />
then 350 g was poured into each test chamber and allowed to settle. The<br />
organic carbon content of the test sediment was 4.2% prior to testing. A<br />
flow-through diluter system delivered test material in water to glass<br />
containers with 120-140 cm 2 bottom surface area each. Test concentrations<br />
were control, 8, 42, 146, 319, and 993 ppm. Intact egg masses were<br />
incubated in Petri dishes containing 20-30 mL of dilution water at 22 °C<br />
until hatching commenced. Newly hatched larvae were allowed to mature<br />
72 hours before testing. Twenty larvae were randomly distributed to each<br />
duplicate test chamber for each of five test concentrations plus the controls.<br />
Larvae were fed daily until emergence of the first adult in each chamber.<br />
Tests were continued until each midge emerged as an adult or larvae were<br />
determined to be dead. The number of winged adults was recorded daily.<br />
The average test duration was 24 days. Total hardness, pH, dissolved<br />
oxygen, and temperature were monitored frequently during the test.<br />
GLP: Yes [ ] No [] ? [X]<br />
Test substance: C11.8 <strong>LAS</strong>; 30.4% activity; mean molecular weight = 346<br />
Remarks: Adults typically emerged 12-14 days after hatching. Control values for adult<br />
emergence were similar to or exceeded the historical average observed in<br />
their laboratory (>90%). Percent emergence was 98, 95, 90, 90, 90, and 73<br />
for the control, 8, 42, 146, 319, and 993 ppm concentrations, respectively.<br />
For comparison, additional flow-through studies were conducted without<br />
sediment (see 4.5.2 (o)). Results indicate that sorption onto sediment<br />
significantly mitigates <strong>LAS</strong> bioavailability.<br />
Reference: Pittinger, C.A., Woltering, D.M., and Masters, J.A. 1989. Bioavailability of<br />
sediment-sorbed and aqueous surfactants to Chironomus riparius (midge).<br />
Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 8:1023-1033.<br />
Reliability: 2 Valid with restrictions.<br />
4.6 TOXICITY TO TERRESTRIAL ORGANISMS<br />
4.6.1 TOXICITY TO SOIL DWELLING ORGANISMS<br />
(a)<br />
Species/Endpoints: See table<br />
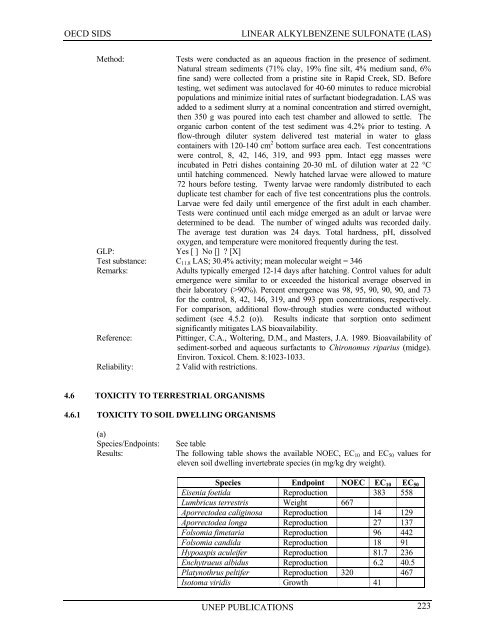
Results: The following table shows the available NOEC, EC10 and EC50 values for<br />
eleven soil dwelling invertebrate species (in mg/kg dry weight).<br />
Species Endpoint NOEC EC10 EC50<br />
Eisenia foetida Reproduction 383 558<br />
Lumbricus terrestris Weight 667<br />
Aporrectodea caliginosa Reproduction 14 129<br />
Aporrectodea longa Reproduction 27 137<br />
Folsomia fimetaria Reproduction 96 442<br />
Folsomia candida Reproduction 18 91<br />
Hypoaspis aculeifer Reproduction 81.7 236<br />
Enchytraeus albidus Reproduction 6.2 40.5<br />
Platynothrus peltifer Reproduction 320 467<br />
Isotoma viridis Growth 41<br />
<strong>UNEP</strong> PUBLICATIONS 223