Numerical Methods Contents - SAM
Numerical Methods Contents - SAM
Numerical Methods Contents - SAM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
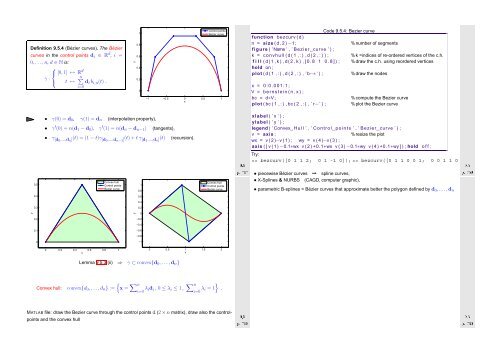
Definition 9.5.4 (Bézier curves). The Bézier<br />
curves in the control points d i ∈ R d , i =<br />
0,...,n, d ∈ N is:<br />
⎧<br />
⎨ [0, 1] ↦→ R d<br />
γ : ∑<br />
⎩ t ↦→<br />
n d i b i,n (t) .<br />
i=0<br />
0.5<br />
0.4<br />
• γ(0) = d 0 , γ(1) = d n (interpolation property),<br />
• γ ′ (0) = n(d 1 − d 0 ), γ ′ (1) = n(d n − d n−1 ) (tangents),<br />
y<br />
1<br />
0.8<br />
0.6<br />
0.4<br />
0.2<br />
0<br />
Control points<br />
Bezier curve<br />
−1 −0.5 0 0.5 1<br />
x<br />
• γ [d0 ,...,d n ] (t) = (1 − t)γ [d 0 ,...,d n−1 ] (t) + t γ [d 1 ,...,d n ](t) (recursion).<br />
Convex hull<br />
Control points<br />
Bezier curve<br />
1<br />
0.8<br />
0.6<br />
Convex hull<br />
Control points<br />
Bezier curve<br />
Ôº º<br />
1 function bezcurv ( d )<br />
Code 9.5.4: Bezier curve<br />
2 n = size ( d , 2 ) −1; % number of segments<br />
3 figure ( ’Name ’ , ’ Bezier curve ’ ) ;<br />
4 k = convhull ( d ( 1 , : ) , d ( 2 , : ) ) ; % k =indices of re-ordered vertices of the c.h.<br />
5 f i l l ( d ( 1 , k ) , d ( 2 , k ) , [ 0 . 8 1 0 . 8 ] ) ; % draw the c.h. using reordered vertices<br />
6 hold on ;<br />
7 plot ( d ( 1 , : ) , d ( 2 , : ) , ’ b−∗ ’ ) ; % draw the nodes<br />
8<br />
9 x = 0 : 0 . 0 0 1 : 1 ;<br />
10 V = b e r n s t e i n ( n , x ) ;<br />
11 bc = d∗V ; % compute the Bezier curve<br />
12 plot ( bc ( 1 , : ) , bc ( 2 , : ) , ’ r−’ ) ; % plot the Bezier curve<br />
13<br />
14 xlabel ( ’ x ’ ) ;<br />
15 ylabel ( ’ y ’ ) ;<br />
16 legend ( ’ Convex H u l l ’ , ’ C o n trol p o i n t s ’ , ’ Bezier curve ’ ) ;<br />
17 v = axis ; % resize the plot<br />
18 wx = v ( 2 )−v ( 1 ) ; wy = v ( 4 )−v ( 3 ) ;<br />
19 axis ( [ v ( 1 ) −0.1∗wx v ( 2 ) +0.1∗wx v ( 3 ) −0.1∗wy v ( 4 ) +0.1∗wy ] ) ; hold o f f ;<br />
Try:<br />
Ôº º<br />
>> bezcurv([0 1 1 2; 0 1 -1 0]); >> bezcurv([0 1 1 0 0 1; 0 0 1 1 0 0]);<br />
• piecewise Bézier curves ➙ spline curves,<br />
• X-Splines & NURBS<br />
(CAGD, computer graphic),<br />
• parametric B-splines = Bézier curves that approximate better the polygon defined by d 0 , ...,d n<br />
0.4<br />
0.3<br />
0.2<br />
y<br />
y<br />
0<br />
0.2<br />
−0.2<br />
−0.4<br />
0.1<br />
−0.6<br />
−0.8<br />
0<br />
−1<br />
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1<br />
x<br />
0 0.5 1 1.5 2<br />
x<br />
Lemma 9.5.3 (ii) ⇒ γ ⊂ convex{d 0 , . ..,d n }<br />
Convex hull: convex{d 0 ,...,d n } :=<br />
{x = ∑ n<br />
i=0 λ id i , 0 ≤ λ i ≤ 1, ∑ n }<br />
i=0 λ i = 1 .<br />
MATLAB file: draw the Bezier curve through the control points d (2 × n matrix), draw also the controlpoints<br />
and the convex hull<br />
Ôº º<br />
Ôº¼ º