Numerical Methods Contents - SAM
Numerical Methods Contents - SAM
Numerical Methods Contents - SAM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Then store G ij (a,b) as triple (i,j, ρ)<br />
The rationale for this convention is to curb the impact of roundoff errors.<br />
Fill-in for QR-decomposition ?<br />
bandwidth<br />
✗<br />
✖<br />
A ∈ C n,n with QR-decomposition A = QR ⇒ m(R) ≤ m(A) (→ Def. 2.6.4)<br />
Example 2.8.14 (QR-based solution of tridiagonal LSE).<br />
✔<br />
✕<br />
Storing orthogonal transformation matrices is usually inefficient !<br />
Algorithm 2.8.11 (Solving linear system of equations by means of QR-decomposition).<br />
Ax = b :<br />
1 QR-decomposition A = QR, computational costs 2 3 n3 + O(n 2 ) (about twice<br />
as expensive as LU-decomposition without pivoting)<br />
2 orthogonal transformation z = Q H b, computational costs 4n 2 + O(n) (in the<br />
case of compact storage of reflections/rotations)<br />
3 Backward substitution, solve Rx = z, computational costs 1 2n(n + 1)<br />
△<br />
Ôº¾¼ ¾º<br />
Elimination of Sub-diagonals by n − 1 successive Givens rotations:<br />
⎛<br />
⎞ ⎛<br />
⎞<br />
⎛<br />
⎞<br />
∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0 0<br />
∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0 0<br />
∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0 0<br />
0 ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0 0<br />
0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0<br />
0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0<br />
0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0<br />
0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0<br />
0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0<br />
G 12<br />
0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0<br />
−−→<br />
0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 0<br />
G 23 G n−1,n<br />
0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0<br />
−−→ · · · −−−−−→<br />
0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0<br />
0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0<br />
⎜<br />
0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0<br />
⎟ ⎜<br />
0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0<br />
⎟<br />
⎜<br />
0 0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗<br />
⎟<br />
⎝0 0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗⎠<br />
⎝0 0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗⎠<br />
⎝0 0 0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗⎠<br />
0 0 0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 0 0 0 ∗ ∗<br />
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ∗<br />
MATLAB code (c,d,e,b = column vectors of length n, n ∈ N, e(n),c(n) not used):<br />
⎛<br />
⎞<br />
d 1 c 1 0 ... 0<br />
e 1 d 2 c 2 .<br />
A =<br />
⎜ 0 e 2 d 3 c 3<br />
⎟ ↔ spdiags([e,d,c],[-1 0 1],n,n)<br />
⎝ . . .. . .. . .. c n−1 ⎠<br />
0 ... 0 e n−1 d n<br />
Ôº¾½½ ¾º<br />
✬<br />
✌ Computing the generalized QR-decomposition A = QR by means of Householder reflections<br />
or Givens rotations is (numerically stable) for any A ∈ C m,n .<br />
✌ For any regular system matrix an LSE can be solved by means of<br />
✫<br />
in a stable manner.<br />
QR-decomposition + orthogonal transformation + backward substitution<br />
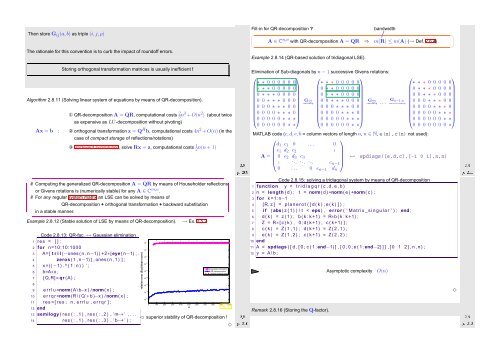
Example 2.8.12 (Stable solution of LSE by means of QR-decomposition). → Ex. 2.5.2<br />
Code 2.8.13: QR-fac. ↔ Gaussian elimination<br />
1 res = [ ] ;<br />
2 for n=10:10:1000<br />
3 A=[ t r i l (−ones ( n , n−1) ) +2∗[eye ( n−1) ; . . .<br />
4 zeros ( 1 , n−1) ] , ones ( n , 1 ) ] ;<br />
5 x=(( −1) . ^ ( 1 : n ) ) ’ ;<br />
6 b=A∗x ;<br />
7 [Q,R]= qr (A) ;<br />
8<br />
9 e r r l u =norm(A \ b−x ) / norm( x ) ;<br />
10 e r r q r =norm(R \ ( Q’∗ b )−x ) / norm( x ) ;<br />
11 res =[ res ; n , e r r l u , e r r q r ] ;<br />
12 end<br />
13 semilogy ( res ( : , 1 ) , res ( : , 2 ) , ’m−∗ ’ , . . .<br />
14 res ( : , 1 ) , res ( : , 3 ) , ’ b−+ ’ ) ;<br />
relative error (Euclidean norm)<br />
10 0<br />
10 −2<br />
10 −4<br />
10 −6<br />
Gaussian elimination<br />
10 −8<br />
QR−decomposition<br />
relative residual norm<br />
10 −10<br />
10 −12<br />
10 −14<br />
10 −16<br />
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000<br />
n<br />
Fig. 25<br />
✩<br />
✪<br />
Ôº¾½¼ ¾º<br />
Remark 2.8.16 (Storing the Q-factor).<br />
✁ superior stability of QR-decomposition !<br />
✸<br />
Code 2.8.15: solving a tridiagonal system by means of QR-decomposition<br />
1 function y = t r i d i a g q r ( c , d , e , b )<br />
2 n = length ( d ) ; t = norm( d ) +norm( e ) +norm( c ) ;<br />
3 for k =1:n−1<br />
4 [R, z ] = p l a n e r o t ( [ d ( k ) ; e ( k ) ] ) ;<br />
5 i f ( abs ( z ( 1 ) ) / t < eps ) , error ( ’ M a trix s i n g u l a r ’ ) ; end ;<br />
6 d ( k ) = z ( 1 ) ; b ( k : k +1) = R∗b ( k : k +1) ;<br />
7 Z = R∗[ c ( k ) , 0 ; d ( k +1) , c ( k +1) ] ;<br />
8 c ( k ) = Z ( 1 , 1 ) ; d ( k +1) = Z ( 2 , 1 ) ;<br />
9 e ( k ) = Z ( 1 , 2 ) ; c ( k +1) = Z ( 2 , 2 ) ;<br />
10 end<br />
11 A = spdiags ( [ d , [ 0 ; c ( 1 : end−1) ] , [ 0 ; 0 ; e ( 1 : end−2) ] ] , [ 0 1 2 ] , n , n ) ;<br />
12 y = A \ b ;<br />
Asymptotic complexity<br />
O(n)<br />
✸<br />
Ôº¾½¾ ¾º