Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Primary Antibodies<br />
Folate Receptor Alpha<br />
Clone BN3.2 New!<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL liquid NCL-L-FRalpha P (HIER)<br />
Folate is a basic component of cell metabolism and DNA synthesis and<br />
repair. It is involved in essential one-carbon transfer reactions and is a<br />
vitamin required by both normal and tumor cells. Folate entry into cells is<br />
facilitated via two different systems: the reduced folate carrier, which<br />
utilizes a bidirectional anion-exchange mechanism, and the folate receptor<br />
system. Folate receptor alpha is a membrane–bound member of the folate<br />
receptor family, facilitating folate transport via a mechanism termed<br />
potocytosis where the receptor is internalized and then recycled back to the<br />
cell membrane. Staining patterns are both membrane and cytoplasmic due<br />
to this mechanism. Members of the folate receptor family share highly<br />
conserved sequences in the open reading frames, but differ in amino acids<br />
in the 5’ untranslated regions and as a consequence can differ in function<br />
and tissue expression. Folate receptor alpha expression is reported to be<br />
highly restricted in normal tissues and only selectively overexpressed in a<br />
limited number of epithelial malignancies.<br />
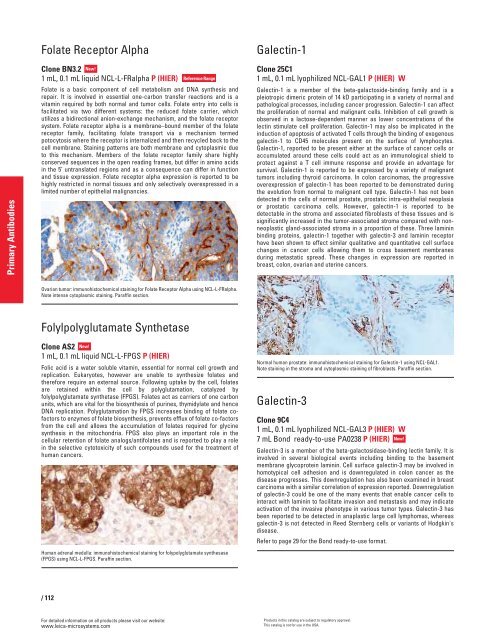
Ovarian tumor: immunohistochemical staining for Folate Receptor Alpha using NCL-L-FRalpha.<br />
Note intense cytoplasmic staining. Paraffin section.<br />
Folylpolyglutamate Synthetase<br />
Clone AS2 New!<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL liquid NCL-L-FPGS P (HIER)<br />
Folic acid is a water soluble vitamin, essential for normal cell g<strong>row</strong>th and<br />
replication. Eukaryotes, however are unable to synthesize folates and<br />
therefore require an external source. Following uptake by the cell, folates<br />
are retained within the cell by polyglutamation, catalyzed by<br />
folylpolyglutamate synthetase (FPGS). Folates act as carriers of one carbon<br />
units, which are vital for the biosynthesis of purines, thymidylate and hence<br />
DNA replication. Polyglutamation by FPGS increases binding of folate cofactors<br />
to enzymes of folate biosynthesis, prevents efflux of folate co-factors<br />
from the cell and allows the accumulation of folates required for glycine<br />
synthesis in the mitochondria. FPGS also plays an important role in the<br />
cellular retention of folate analogs/antifolates and is reported to play a role<br />
in the selective cytotoxicity of such compounds used for the treatment of<br />
human cancers.<br />
Human adrenal medulla: immunohistochemical staining for folypolyglutamate synthesase<br />
(FPGS) using NCL-L-FPGS. Paraffin section.<br />
/ 112<br />
For detailed information on all products please visit our website:<br />
www.leica-microsystems.com<br />
Reference Range<br />
Galectin-1<br />
Clone 25C1<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL lyophilized NCL-GAL1 P (HIER) W<br />
Galectin-1 is a member of the beta-galactoside-binding family and is a<br />
pleiotropic dimeric protein of 14 kD participating in a variety of normal and<br />
pathological processes, including cancer progression. Galectin-1 can affect<br />
the proliferation of normal and malignant cells. Inhibition of cell g<strong>row</strong>th is<br />
observed in a lactose-dependent manner as lower concentrations of the<br />
lectin stimulate cell proliferation. Galectin-1 may also be implicated in the<br />
induction of apoptosis of activated T cells through the binding of exogenous<br />
galectin-1 to CD45 molecules present on the surface of lymphocytes.<br />
Galectin-1, reported to be present either at the surface of cancer cells or<br />
accumulated around these cells could act as an immunological shield to<br />
protect against a T cell immune response and provide an advantage for<br />
survival. Galectin-1 is reported to be expressed by a variety of malignant<br />
tumors including thyroid carcinoma. In colon carcinomas, the progressive<br />
overexpression of galectin-1 has been reported to be demonstrated during<br />
the evolution from normal to malignant cell type. Galectin-1 has not been<br />
detected in the cells of normal prostate, prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia<br />
or prostatic carcinoma cells. However, galectin-1 is reported to be<br />
detectable in the stroma and associated fibroblasts of these tissues and is<br />
significantly increased in the tumor-associated stroma compared with nonneoplastic<br />
gland-associated stroma in a proportion of these. Three laminin<br />
binding proteins, galectin-1 together with galectin-3 and laminin receptor<br />
have been shown to effect similar qualitative and quantitative cell surface<br />
changes in cancer cells allowing them to cross basement membranes<br />
during metastatic spread. These changes in expression are reported in<br />
breast, colon, ovarian and uterine cancers.<br />
Normal human prostate: immunohistochemical staining for Galectin-1 using NCL-GAL1.<br />
Note staining in the stroma and cytoplasmic staining of fibroblasts. Paraffin section.<br />
Galectin-3<br />
Clone 9C4<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL lyophilized NCL-GAL3 P (HIER) W<br />
7 mL Bond ready-to-use PA0238 P (HIER) New!<br />
Galectin-3 is a member of the beta-galactosidase-binding lectin family. It is<br />
involved in several biological events including binding to the basement<br />
membrane glycoprotein laminin. Cell surface galectin-3 may be involved in<br />
homotypical cell adhesion and is downregulated in colon cancer as the<br />
disease progresses. This downregulation has also been examined in breast<br />
carcinoma with a similar correlation of expression reported. Downregulation<br />
of galectin-3 could be one of the many events that enable cancer cells to<br />
interact with laminin to facilitate invasion and metastasis and may indicate<br />
activation of the invasive phenotype in various tumor types. Galectin-3 has<br />
been reported to be detected in anaplastic large cell lymphomas, whereas<br />
galectin-3 is not detected in Reed Sternberg cells or variants of Hodgkin's<br />
disease.<br />
Refer to page 29 for the Bond ready-to-use format.<br />
Products in this catalog are subject to regulatory approval.<br />
This catalog is not for use in the USA.