Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Primary Antibodies<br />
CD166 (ALCAM)<br />
Clone MOG/07<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL lyophilized NCL-CD166 P (HIER)<br />
The human CD166 molecule, also known as activated leukocyte cell<br />
adhesion molecule (ALCAM), is a glycoprotein of 100 kD that functions as a<br />
ligand for the CD6 molecule. It is the human homolog of the chicken neural<br />
adhesion molecule, BEN/SC-1/DM-GRASP, the rat molecule, KG-CAM, and<br />
the fish protein, neurolin. The CD166 molecule is reported to be expressed by<br />
a subset of activated leukocytes. CD166/CD6 interactions may play a role in<br />
the binding of T and B cells to activated leukocytes as well as in interactions<br />
between cells of the nervous system involving neurite extension of the<br />
neurons. The CD166 molecule is also expressed in a number of other cell<br />
types including activated monocytes, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, neurons,<br />
melanoma cells and also in sweat and sebaceous glands. CD166 protein<br />
expression is reported to be upregulated in a cell line deriving from a<br />
metastasizing melanoma. It is also reported that CD166 protein may play a<br />
role in T cell development in the thymus.<br />
CD168 (RHAMM)<br />
Clone 2D6<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-CD168 F P (HIER)<br />
The CD168 molecule, also known as RHAMM/IHABP (receptor for<br />
hyaluronic acid mediated motility/intracellular hyaluronic acid binding<br />
protein), is a ubiquitously expressed filamentous, cytoskeletal accessory<br />
protein. It is not, as originally reported, a cell surface receptor. However, in<br />
some cancers, it is reported that the expression of cell surface variants of<br />
CD168 is closely correlated with tumor progression. The CD168 molecule<br />
plays a role in cell signalling, migration and adhesion via interactions with<br />
hyaluronan, microtubules, actin, calmodulin and components of the<br />
extracellular regulated kinase (erk) signalling pathway. CD168 appears to<br />
have an important role in human sperm motility. In the brain, the CD168<br />
molecule is reported to be expressed in the majority of neurons and in many<br />
oligodendrocytes where it has an effect on astrocyte motility, neurite<br />
migration and axonal g<strong>row</strong>th. CD168 antigen is necessary for migration of<br />
smooth muscle cells after wound injury and it has been associated with<br />
adult wound fibroplasias. Reports indicate that CD168 antigen is detected at<br />
varying levels in normal breast epithelium but in breast cancers, strong<br />
expression has been observed particularly in well-differentiated grade 1<br />
ductal carcinomas, whereas high grade cancers displayed significantly<br />
lower expression. CD168 is also reported to be expressed at low frequency<br />
in non-cancerous gastric mucosa and in 74 percent of gastric cancers<br />
where it is associated with malignant progression.<br />
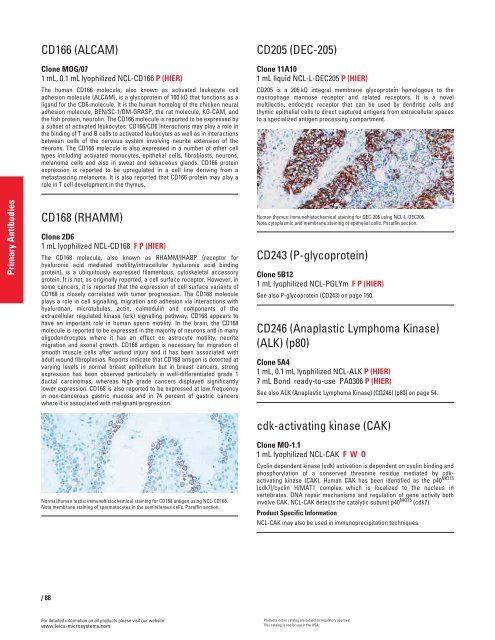
Normal human testis: immunohistochemical staining for CD168 antigen using NCL-CD168.<br />
Note membrane staining of spermatocytes in the seminiferous cells. Paraffin section.<br />
/88<br />
For detailed information on all products please visit our website:<br />
www.leica-microsystems.com<br />
CD205 (DEC-205)<br />
Clone 11A10<br />
1 mL liquid NCL-L-DEC205 P (HIER)<br />
CD205 is a 205 kD integral membrane glycoprotein homologous to the<br />
macrophage mannose receptor and related receptors. It is a novel<br />
multilectin, endocytic receptor that can be used by dendritic cells and<br />
thymic epithelial cells to direct captured antigens from extracellular spaces<br />
to a specialized antigen processing compartment.<br />
Human thymus: immunohistochemical staining for DEC-205 using NCL-L-DEC205.<br />
Note cytoplasmic and membrane staining of epithelial cells. Paraffin section.<br />
CD243 (P-glycoprotein)<br />
Clone 5B12<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-PGLYm F P (HIER)<br />
See also P-glycoprotein (CD243) on page 150.<br />
CD246 (Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase)<br />
(ALK) (p80)<br />
Clone 5A4<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL lyophilized NCL-ALK P (HIER)<br />
7 mL Bond ready-to-use PA0306 P (HIER)<br />
See also ALK (Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase) (CD246) (p80) on page 54.<br />
cdk-activating kinase (CAK)<br />
Clone MO-1.1<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-CAK FWO<br />
Cyclin dependent kinase (cdk) activation is dependent on cyclin binding and<br />
phosphorylation of a conserved threonine residue mediated by cdkactivating<br />
kinase (CAK). Human CAK has been identified as the p40 MO15<br />
(cdk7)/cyclin H/MAT1 complex which is localized to the nucleus in<br />
vertebrates. DNA repair mechanisms and regulation of gene activity both<br />
involve CAK. NCL-CAK detects the catalytic subunit p40 MO15 (cdk7).<br />
Product Specific Information<br />
NCL-CAK may also be used in immunoprecipitation techniques.<br />
Products in this catalog are subject to regulatory approval.<br />
This catalog is not for use in the USA.