Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Cathepsin G<br />
Clone 19C3<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-CATH-G P (HIER) W<br />
Cathepsin G expression in normal tissues is restricted to granulocytes,<br />
especially neutrophils. However, mononuclear phagocytes have been<br />
demonstrated to bind and internalize proteases from neutrophils. Cathepsin<br />
G is located in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes which contain<br />
specialized azurophil granules together with two other serine proteases;<br />
elastase and hepsin. These three proteases may participate in the killing<br />
and digestion of engulfed pathogens and in connective tissue remodelling at<br />
sites of inflammation. Cathepsin G is also reported to be expressed in acute<br />
and chronic myeloid leukemias whereas acute lymphoblastic or chronic<br />
lymphocytic leukemias are negative for this protein.<br />
Human tonsil: immunohistochemical staining for cathepsin G using NCL-CATH-G. Note intense<br />
membrane staining of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Paraffin section.<br />
Cathepsin L<br />
Clone 13C2<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-CATH-L P<br />
Cathepsin L is a lysosomal cysteine protease which plays a major role in<br />
intracellular protein catabolism. It exhibits the most potent collagenolytic<br />
and elastinolytic activity of any of the cathepsins in vitro. It can inactivate<br />
alpha-1 protease inhibitor which controls human neutrophil elastase activity<br />
in vitro. Cathepsin L has been implicated in a number of pathological<br />
processes including myofibrial necrosis in myopathies and in myocardial<br />
ischemia and also in the renal tubular response to proteinuria. Cathepsin L is<br />
present in all normal cell types but, in general, increased expression occurs<br />
in cancers. The highest observed levels of Cathepsin L are to be found in<br />
kidney and testicular tumors, with very high levels reported to be detected in<br />
non-small cell carcinomas of the lung and above normal levels expressed in<br />
breast, ovarian, colonic, adrenal, bladder, prostate and thyroid cancers.<br />
Cathepsin L, serine protease (uPA), protease inhibitor (PAI-1) as well as<br />
other proteases play an important role in cancer invasion by their ability to<br />
destroy the surrounding extracellular matrix through their respective<br />
proteolytic activities.<br />
Human liver: immunohistochemical staining for cathepsin L using NCL-CATH-L. Note granular<br />
cytoplasmic staining of a proportion of hepatocytes. Paraffin section.<br />
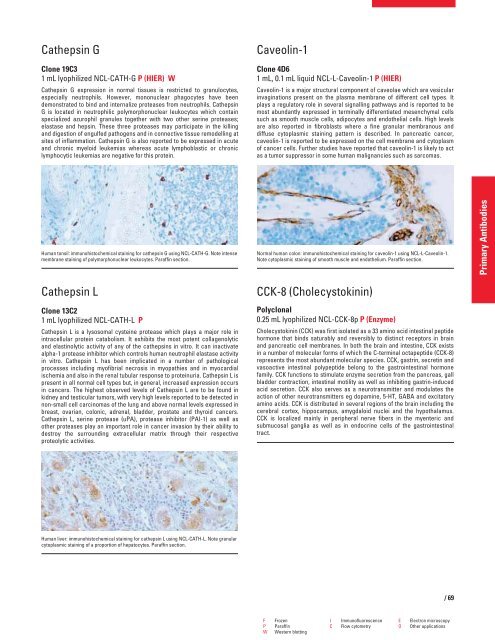
Caveolin-1<br />
Clone 4D6<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL liquid NCL-L-Caveolin-1 P (HIER)<br />
Caveolin-1 is a major structural component of caveolae which are vesicular<br />
invaginations present on the plasma membrane of different cell types. It<br />
plays a regulatory role in several signalling pathways and is reported to be<br />
most abundantly expressed in terminally differentiated mesenchymal cells<br />
such as smooth muscle cells, adipocytes and endothelial cells. High levels<br />
are also reported in fibroblasts where a fine granular membranous and<br />
diffuse cytoplasmic staining pattern is described. In pancreatic cancer,<br />
caveolin-1 is reported to be expressed on the cell membrane and cytoplasm<br />
of cancer cells. Further studies have reported that caveolin-1 is likely to act<br />
as a tumor suppressor in some human malignancies such as sarcomas.<br />
Normal human colon: immunohistochemical staining for caveolin-1 using NCL-L-Caveolin-1.<br />
Note cytoplasmic staining of smooth muscle and endothelium. Paraffin section.<br />
CCK-8 (Cholecystokinin)<br />
Polyclonal<br />
0.25 mL lyophilized NCL-CCK-8p P (Enzyme)<br />
Cholecystokinin (CCK) was first isolated as a 33 amino acid intestinal peptide<br />
hormone that binds saturably and reversibly to distinct receptors in brain<br />
and pancreatic cell membranes. In both the brain and intestine, CCK exists<br />
in a number of molecular forms of which the C-terminal octapeptide (CCK-8)<br />
represents the most abundant molecular species. CCK, gastrin, secretin and<br />
vasoactive intestinal polypeptide belong to the gastrointestinal hormone<br />
family. CCK functions to stimulate enzyme secretion from the pancreas, gall<br />
bladder contraction, intestinal motility as well as inhibiting gastrin-induced<br />
acid secretion. CCK also serves as a neurotransmitter and modulates the<br />
action of other neurotransmitters eg dopamine, 5-HT, GABA and excitatory<br />
amino acids. CCK is distributed in several regions of the brain including the<br />
cerebral cortex, hippocampus, amygdaloid nuclei and the hypothalamus.<br />
CCK is localized mainly in peripheral nerve fibers in the myenteric and<br />
submucosal ganglia as well as in endocrine cells of the gastrointestinal<br />
tract.<br />
F Frozen I Immunofluorescence E Electron microscopy<br />
P Paraffin C Flow cytometry O Other applications<br />
W Western blotting<br />
/69<br />
Primary Antibodies