Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Vascular Endothelial G<strong>row</strong>th Factor<br />
Receptor-3<br />
Clone KLT9<br />
1 mL liquid NCL-L-VEGFR-3 P<br />
VEGFR-3 (FLT4) is a receptor tyrosine kinase similar in structure to VEGFR-1<br />
and VEGFR-2 but does not bind VEGF. However, the two known ligands have<br />
a high degree of homology to VEGF and are known as VEGF-C and VEGF-D.<br />
VEGFR-3 is reported to be found in many tissues including lung, intestine,<br />
brain and placenta (syncytiotrophoblasts). Throughout embryogenesis,<br />
VEGFR-3 mRNA is expressed in most endothelial cells, whilst being<br />
restricted to lymphatic vessels later in development. It appears to play an<br />
important role in the normal development of blood and lymphatic vessels. In<br />
tumors, expression has been reported in blood capillary endothelium and<br />
VEGFR-3 is thought to be involved in angiogenesis during tumor g<strong>row</strong>th.<br />
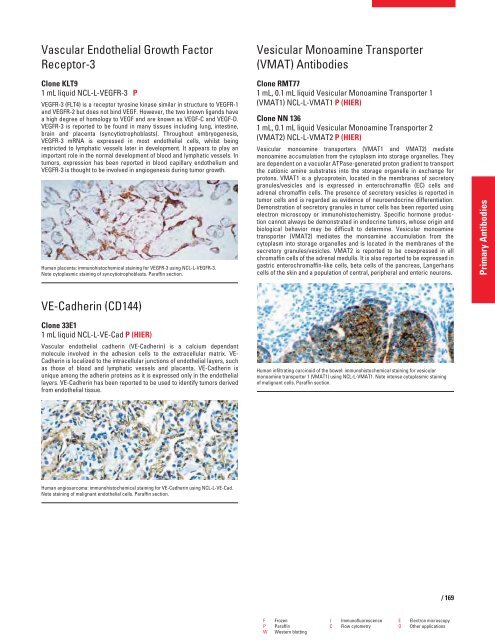
Human placenta: immunohistochemical staining for VEGFR-3 using NCL-L-VEGFR-3.<br />
Note cytoplasmic staining of syncytiotrophoblasts. Paraffin section.<br />
VE-Cadherin (CD144)<br />
Clone 33E1<br />
1 mL liquid NCL-L-VE-Cad P (HIER)<br />
Vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-Cadherin) is a calcium dependant<br />
molecule involved in the adhesion cells to the extracellular matrix. VE-<br />
Cadherin is localized to the intracellular junctions of endothelial layers, such<br />
as those of blood and lymphatic vessels and placenta. VE-Cadherin is<br />
unique among the adherin proteins as it is expressed only in the endothelial<br />
layers. VE-Cadherin has been reported to be used to identify tumors derived<br />
from endothelial tissue.<br />
Human angiosarcoma: immunohistochemical staining for VE-Cadherin using NCL-L-VE-Cad.<br />
Note staining of malignant endothelial cells. Paraffin section.<br />
Vesicular Monoamine Transporter<br />
(VMAT) Antibodies<br />
Clone RMT77<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL liquid Vesicular Monoamine Transporter 1<br />
(VMAT1) NCL-L-VMAT1 P (HIER)<br />
Clone NN 136<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL liquid Vesicular Monoamine Transporter 2<br />
(VMAT2) NCL-L-VMAT2 P (HIER)<br />
Vesicular monoamine transporters (VMAT1 and VMAT2) mediate<br />
monoamine accumulation from the cytoplasm into storage organelles. They<br />
are dependent on a vacuolar ATPase-generated proton gradient to transport<br />
the cationic amine substrates into the storage organelle in exchange for<br />
protons. VMAT1 is a glycoprotein, located in the membranes of secretory<br />
granules/vesicles and is expressed in enterochromaffin (EC) cells and<br />
adrenal chromaffin cells. The presence of secretory vesicles is reported in<br />
tumor cells and is regarded as evidence of neuroendocrine differentiation.<br />
Demonstration of secretory granules in tumor cells has been reported using<br />
electron microscopy or immunohistochemistry. Specific hormone production<br />
cannot always be demonstrated in endocrine tumors, whose origin and<br />
biological behavior may be difficult to determine. Vesicular monoamine<br />
transporter (VMAT2) mediates the monoamine accumulation from the<br />
cytoplasm into storage organelles and is located in the membranes of the<br />
secretory granules/vesicles. VMAT2 is reported to be coexpressed in all<br />
chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. It is also reported to be expressed in<br />
gastric enterochromaffin-like cells, beta cells of the pancreas, Langerhans<br />
cells of the skin and a population of central, peripheral and enteric neurons.<br />
Human infiltrating carcinoid of the bowel: immunohistochemical staining for vesicular<br />
monoamine transporter 1 (VMAT1) using NCL-L-VMAT1. Note intense cytoplasmic staining<br />
of malignant cells. Paraffin section.<br />
F Frozen I Immunofluorescence E Electron microscopy<br />
P Paraffin C Flow cytometry O Other applications<br />
W Western blotting<br />
/ 169<br />
Primary Antibodies