Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
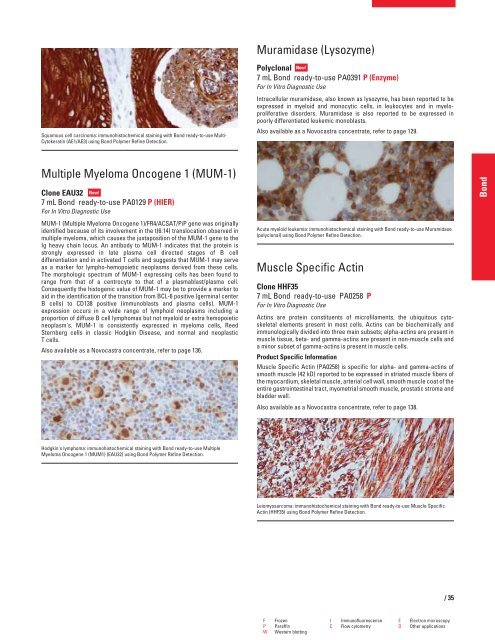
Squamous cell carcinoma: immunohistochemical staining with Bond ready-to-use Multi-<br />
Cytokeratin (AE1/AE3) using Bond Polymer Refine Detection.<br />
Multiple Myeloma Oncogene 1 (MUM-1)<br />
Clone EAU32 New!<br />
7 mL Bond ready-to-use PA0129 P (HIER)<br />
For In Vitro Diagnostic Use<br />
MUM-1 (Multiple Myeloma Oncogene 1)/FR4/ACSAT/PiP gene was originally<br />
identified because of its involvement in the t(6:14) translocation observed in<br />
multiple myeloma, which causes the juxtaposition of the MUM-1 gene to the<br />
Ig heavy chain locus. An antibody to MUM-1 indicates that the protein is<br />
strongly expressed in late plasma cell directed stages of B cell<br />
differentiation and in activated T cells and suggests that MUM-1 may serve<br />
as a marker for lympho-hemopoietic neoplasms derived from these cells.<br />
The morphologic spectrum of MUM-1 expressing cells has been found to<br />
range from that of a centrocyte to that of a plasmablast/plasma cell.<br />
Consequently the histogenic value of MUM-1 may be to provide a marker to<br />
aid in the identification of the transition from BCL-6 positive (germinal center<br />
B cells) to CD138 positive (immunoblasts and plasma cells). MUM-1<br />
expression occurs in a wide range of lymphoid neoplasms including a<br />
proportion of diffuse B cell lymphomas but not myeloid or extra hemopoietic<br />
neoplasm's. MUM-1 is consistently expressed in myeloma cells, Reed<br />
Sternberg cells in classic Hodgkin Disease, and normal and neoplastic<br />
T cells.<br />
Also available as a Novocastra concentrate, refer to page 136.<br />
Hodgkin's lymphoma: immunohistochemical staining with Bond ready-to-use Multiple<br />
Myeloma Oncogene 1 (MUM1) (EAU32) using Bond Polymer Refine Detection.<br />
Muramidase (Lysozyme)<br />
Polyclonal New!<br />
7 mL Bond ready-to-use PA0391 P (Enzyme)<br />
For In Vitro Diagnostic Use<br />
Intracellular muramidase, also known as lysozyme, has been reported to be<br />
expressed in myeloid and monocytic cells, in leukocytes and in myeloproliferative<br />
disorders. Muramidase is also reported to be expressed in<br />
poorly differentiated leukemic monoblasts.<br />
Also available as a Novocastra concentrate, refer to page 129.<br />
Acute myeloid leukemia: immunohistochemical staining with Bond ready-to-use Muramidase<br />
(polyclonal) using Bond Polymer Refine Detection.<br />
Muscle Specific Actin<br />
Clone HHF35<br />
7 mL Bond ready-to-use PA0258 P<br />
For In Vitro Diagnostic Use<br />
Actins are protein constituents of microfilaments, the ubiquitous cytoskeletal<br />
elements present in most cells. Actins can be biochemically and<br />
immunologically divided into three main subsets; alpha-actins are present in<br />
muscle tissue, beta- and gamma-actins are present in non-muscle cells and<br />
a minor subset of gamma-actins is present in muscle cells.<br />
Product Specific Information<br />
Muscle Specific Actin (PA0258) is specific for alpha- and gamma-actins of<br />
smooth muscle (42 kD) reported to be expressed in striated muscle fibers of<br />
the myocardium, skeletal muscle, arterial cell wall, smooth muscle coat of the<br />
entire gastrointestinal tract, myometrial smooth muscle, prostatic stroma and<br />
bladder wall.<br />
Also available as a Novocastra concentrate, refer to page 138.<br />
Leiomyosarcoma: immunohistochemical staining with Bond ready-to-use Muscle Specific<br />
Actin (HHF35) using Bond Polymer Refine Detection.<br />
F Frozen I Immunofluorescence E Electron microscopy<br />
P Paraffin C Flow cytometry O Other applications<br />
W Western blotting<br />
/35<br />
Bond