Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
Labelling Review row-Online
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
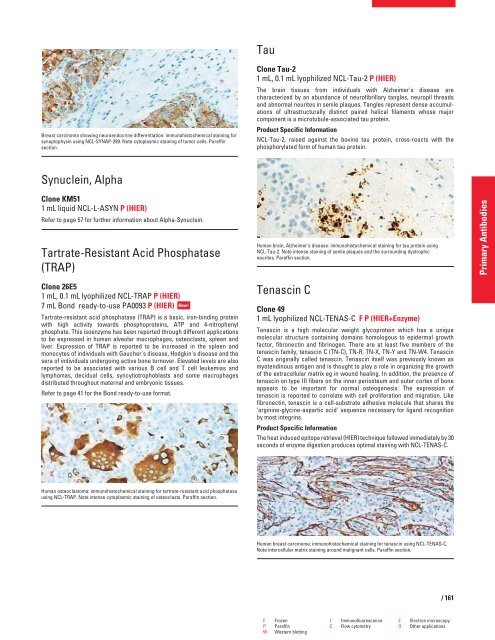
Breast carcinoma showing neuroendocrine differentiation: immunohistochemical staining for<br />
synaptophysin using NCL-SYNAP-299. Note cytoplasmic staining of tumor cells. Paraffin<br />
section.<br />
Synuclein, Alpha<br />
Clone KM51<br />
1 mL liquid NCL-L-ASYN P (HIER)<br />
Refer to page 57 for further information about Alpha-Synuclein.<br />
Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase<br />
(TRAP)<br />
Clone 26E5<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL lyophilized NCL-TRAP P (HIER)<br />
7 mL Bond ready-to-use PA0093 P (HIER)<br />
New!<br />
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) is a basic, iron-binding protein<br />
with high activity towards phosphoproteins, ATP and 4-nitrophenyl<br />
phosphate. This isoenzyme has been reported through different applications<br />
to be expressed in human alveolar macrophages, osteoclasts, spleen and<br />
liver. Expression of TRAP is reported to be increased in the spleen and<br />
monocytes of individuals with Gaucher's disease, Hodgkin's disease and the<br />
sera of individuals undergoing active bone turnover. Elevated levels are also<br />
reported to be associated with various B cell and T cell leukemias and<br />
lymphomas, decidual cells, syncytiotrophoblasts and some macrophages<br />
distributed throughout maternal and embryonic tissues.<br />
Refer to page 41 for the Bond ready-to-use format.<br />
Human osteoclastoma: immunohistochemical staining for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase<br />
using NCL-TRAP. Note intense cytoplasmic staining of osteoclasts. Paraffin section.<br />
Tau<br />
Clone Tau-2<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL lyophilized NCL-Tau-2 P (HIER)<br />
The brain tissues from individuals with Alzheimer's disease are<br />
characterized by an abundance of neurofibrillary tangles, neuropil threads<br />
and abnormal neurites in senile plaques. Tangles represent dense accumulations<br />
of ultrastructurally distinct paired helical filaments whose major<br />
component is a microtubule-associated tau protein.<br />
Product Specific Information<br />
NCL-Tau-2, raised against the bovine tau protein, cross-reacts with the<br />
phosphorylated form of human tau protein.<br />
Human brain, Alzheimer's disease: immunohistochemical staining for tau protein using<br />
NCL-Tau-2. Note intense staining of senile plaques and the surrounding dystrophic<br />
neurites. Paraffin section.<br />
Tenascin C<br />
Clone 49<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-TENAS-C F P (HIER+Enzyme)<br />
Tenascin is a high molecular weight glycoprotein which has a unique<br />
molecular structure containing domains homologous to epidermal g<strong>row</strong>th<br />
factor, fibronectin and fibrinogen. There are at least five members of the<br />
tenascin family, tenascin C (TN-C), TN-R, TN-X, TN-Y and TN-W4. Tenascin<br />
C was originally called tenascin. Tenascin itself was previously known as<br />
myotendinous antigen and is thought to play a role in organizing the g<strong>row</strong>th<br />
of the extracellular matrix eg in wound healing. In addition, the presence of<br />
tenascin on type III fibers on the inner periosteum and outer cortex of bone<br />
appears to be important for normal osteogenesis. The expression of<br />
tenascin is reported to correlate with cell proliferation and migration. Like<br />
fibronectin, tenascin is a cell-substrate adhesive molecule that shares the<br />
‘arginine-glycine-aspartic acid' sequence necessary for ligand recognition<br />
by most integrins.<br />
Product Specific Information<br />
The heat induced epitope retrieval (HIER) technique followed immediately by 30<br />
seconds of enzyme digestion produces optimal staining with NCL-TENAS-C.<br />
Human breast carcinoma: immunohistochemical staining for tenascin using NCL-TENAS-C.<br />
Note intercellular matrix staining around malignant cells. Paraffin section.<br />
F Frozen I Immunofluorescence E Electron microscopy<br />
P Paraffin C Flow cytometry O Other applications<br />
W Western blotting<br />
/ 161<br />
Primary Antibodies