- Page 6:
w-\>\V
- Page 10 and 11:
Proprietà letteraria DELLA Societ
- Page 12 and 13:
IV non troverà nemmeno traccia del
- Page 15 and 16:
INTRODUZIONE vJli studi geometrici,
- Page 17 and 18:
— 3 — IIF. Lo spazio di piani,
- Page 19 and 20:
— 5 — fascio, chiamando proprio
- Page 21 and 22:
— 7 — Segue che i punti impropr
- Page 23 and 24:
(segue da b) e d) purché sulle due
- Page 25 and 26:
— 11 — elementi corrispondenti
- Page 27 and 28:
stesso piano n. Fra le altre rette
- Page 29 and 30:
— 15 — a') Ritornando alla figu
- Page 31 and 32:
— 17 — E sembra appunto che gli
- Page 33 and 34:
— 19 — ha dunque per corrispond
- Page 35 and 36:
— 21 — quadrato; negli ultimi q
- Page 37 and 38:
— 23 — diversi, sono Vuno proie
- Page 39 and 40:
— 25 — nel piano PSA, devono se
- Page 41 and 42:
— 27 — due trilateri omologici
- Page 43 and 44:
— 29 — problema generalmente no
- Page 45 and 46:
— 31 — Parte Prima. Forme di pr
- Page 47 and 48:
— 33 — forma e senza oltrepassa
- Page 49 and 50:
— 35 — Noi possiamo far ciò se
- Page 51 and 52:
— 37 — regione (+) appartengono
- Page 53 and 54:
— 39 — 2) che ogni elemento del
- Page 55 and 56:
— 41 — '23, 34 . . . tutti ugua
- Page 57 and 58:
— espili ampia che chiameremo A^]
- Page 59 and 60:
— 45 — furono dette di prima sp
- Page 61 and 62:
— 47 — Col metodo da n ad n -]-
- Page 63 and 64:
— 49 — 11) Attribuendo ai punti
- Page 65 and 66:
— 51 — scini con se il proprio
- Page 67 and 68:
— 53 — piani a, ^ è determinat
- Page 69 and 70:
— 55 — ÌA1A2M) := -; si ha di
- Page 71 and 72:
— 57 — denza biunivoca che vien
- Page 73 and 74:
— 59 — la figura da un punto 8
- Page 75 and 76:
— 61 — Il procedimento si esten
- Page 77 and 78:
— 63 — 10) Nel caso particolare
- Page 79 and 80:
— 65 — (cc^y) senay senaó nel
- Page 81 and 82:
— 67 — ( A Ti C^ infatti se il
- Page 83 and 84:
— 69 — ordinata e, come facilme
- Page 85 and 86:
dove si è posto per brevità — 7
- Page 87 and 88:
— 73 — dinate proiettive ^',, A
- Page 89 and 90:
— 75 — sopra nominati, ad es. d
- Page 91 and 92:
— 77 — dicono coniugati armonic
- Page 93 and 94:
— 79 — omologici e precisamente
- Page 95 and 96:
— 81 — In un gruppo armonico di
- Page 97 and 98:
— 83 - ^ = — • Ed operando or
- Page 99 and 100:
— 85 — notiamo che il punto med
- Page 101 and 102:
— 87 — grado (2'), le cui radic
- Page 103 and 104:
— so- sia divisa armonicamente da
- Page 105 and 106:
— 91 — Capitolo II. Proiettivit
- Page 107 and 108:
— 93 — doppio rapporto dei quat
- Page 109 and 110:
- 95 - corrispondono due elementi,
- Page 111 and 112:
— 97 — ad es., Xo
- Page 113 and 114:
— 99 — cedente prova di più, c
- Page 115 and 116:
— 101 — di X uguaglia il doppio
- Page 117 and 118:
— 103 — Se un punto sopra u va
- Page 119 and 120:
— 105 — e quindi, prendendo le
- Page 121 and 122:
— 107 — da u' ad u. Il punto uu
- Page 123 and 124:
— 109 — E importante notare che
- Page 125 and 126:
S'. Servendoci di questo, noi possi
- Page 127 and 128:
— 113 — liari {8 ed 8\ oppure s
- Page 129 and 130:
— 115 — u'. 1 punti M, 0, N si
- Page 131 and 132:
— 117 — 71. Elementi uniti di u
- Page 133 and 134:
— 119 — della proiettivita ABC
- Page 135 and 136:
— 121 — proiettività parabolic
- Page 137 and 138:
— 123 — A, B, C . . . della cir
- Page 139 and 140:
— 125 — Se nella proiettività
- Page 141 and 142:
— 127 — è omologico al triango
- Page 143 and 144:
— 129 — Supponiamo, al contrari
- Page 145 and 146:
— 131 — 81. Equazione deiriiivo
- Page 147 and 148:
— 133 — cìenti delle (4). Con
- Page 149 and 150:
— 135 — il teorema duale) la in
- Page 151 and 152:
— 137 — la involuzione appartie
- Page 153 and 154:
— 139 — Se Z7 è punto doppio d
- Page 155 and 156:
— 141 — La involuzione circolar
- Page 157 and 158:
— 143 — delle due direzioni ass
- Page 159 and 160:
— 145 — opposti del triangolo,
- Page 161 and 162:
— 147 — menti (n.** 68), od in
- Page 163 and 164:
— 149 — dalla determinazione do
- Page 165 and 166:
— 151 — distanza. Qua!' è il m
- Page 167 and 168:
— 153 — ed è iperbolica, parab
- Page 169 and 170:
ossia — ^ — 155 = i + i_ y —
- Page 171 and 172:
— 157 — Parte Seconda. Geometri
- Page 173 and 174:
— 159 — vertice, saranno negati
- Page 175 and 176:
— 161 — Proiettiamo i punti Pi,
- Page 177 and 178:
— 163 — la quale esprime che i
- Page 179 and 180:
— 165 — ad es. sotto la forma (
- Page 181 and 182:
— 167 — e la medesima relazione
- Page 183 and 184:
— 169 — Di qua si deduce subito
- Page 185 and 186:
— 171 - gnano polinomi contenenti
- Page 187 and 188:
— 173 — 5) Risolvere i problemi
- Page 189 and 190:
— 175 — si può costruire una s
- Page 191 and 192:
— 177 — sce un vettore A B ugua
- Page 193 and 194:
— 179 — ' sulle relazioni (a),
- Page 195 and 196:
— 181 — determinare. Ricordiamo
- Page 197 and 198:
— 183 — ed il termine noto, i r
- Page 199 and 200:
— 185 — questa convenzione cost
- Page 201 and 202:
— 187 — è espressa dall' annul
- Page 203 and 204:
— 189 — Pi Q, si inverta il ver
- Page 205 and 206:
— 191 — Osseryazìone. — La c
- Page 207 and 208:
— 193 — un punto (n.° 89), rif
- Page 209 and 210:
— 195 — torno chiuso curvilineo
- Page 211 and 212:
ossia (1) — 197 — y = h -^ Y, l
- Page 213 and 214:
— 199 — Ma per le (1) X = x' -^
- Page 215 and 216:
— 201 — Esercìzi. — 1) Come
- Page 217 and 218:
o meglio — 203 — (2') Xy — Yx
- Page 219 and 220:
— 205 — Questa è soddisfatta,
- Page 221 and 222:
— 207 — Come le coordinate omog
- Page 223 and 224:
— 209 — fondamentali sulla mutu
- Page 225 and 226:
Dunque : V equazione ( in coordinat
- Page 227 and 228:
— 213 — di numeri, e le ^ rette
- Page 229 and 230:
— 215 — UN. La ipotesi è dunqu
- Page 231 and 232:
— 217 — H punto Z ha le coordin
- Page 233 and 234:
— 219 — Riunendo questa alle (1
- Page 235 and 236:
— 221 — di un piano^ valgono an
- Page 237 and 238:
— 223 — cati per convenienti fa
- Page 239 and 240:
— 225 — Esercizi, — 1) Assunt
- Page 241 and 242:
— 227 — che non riesca possibil
- Page 243 and 244:
— 229 — I.'' Definire e studiar
- Page 245 and 246:
— 231 — 141. Invariabilità del
- Page 247 and 248:
— 233 — curva, e si riguarderan
- Page 249 and 250:
— 235 — trica a cui obbedisce u
- Page 251 and 252:
— 237 — del primo sistema; i pu
- Page 253 and 254:
— 239 — nazione di A:; e la ope
- Page 255 and 256:
— 241 — quando siano assegnate
- Page 257 and 258:
— 243 — punti dovrà tendere a
- Page 259 and 260:
% — 245 — continuità, si consi
- Page 261 and 262:
— 247 — un cerchio, il cui cent
- Page 263 and 264:
— 249 — Per ogni valore di
- Page 265 and 266:
— 251 — • Il lettore verifich
- Page 267 and 268:
— 253 — E facile caratterizzare
- Page 269 and 270:
i — 255 — ha la stessa potenza
- Page 271 and 272:
— 257 — nati potrebbero riguard
- Page 273 and 274:
— 259 — superiori o inferiori.
- Page 275 and 276:
— 261 - punti B, B' di ordinate y
- Page 277 and 278:
e fatto z - 263 —
- Page 279 and 280:
— 265 — delle note disuguaglian
- Page 281 and 282:
— 267 — retta x sopra cui quest
- Page 283 and 284:
— 269 — \si OA perpendicolare a
- Page 285 and 286:
i ossia se — 271 — a'^ ^ \ x'^
- Page 287 and 288:
— 273 — cerchio mobile in un de
- Page 289 and 290:
i — 275 — 6) Un' altra generazi
- Page 291 and 292:
I — 277 — 7t^ n\ proiettando i
- Page 293 and 294:
— 279 — proiettino da S, S' uno
- Page 295 and 296:
— 281 — lora A', B', C, D' sono
- Page 297 and 298:
i — 283 — Ma allora applicando
- Page 299 and 300:
— 285 — e viceversa^ ed ogni re
- Page 301 and 302:
I — 287 — (dove Aik ^ il comple
- Page 303 and 304:
— 289 — * Osservazione II. —
- Page 305 and 306:
— 291 — lasciano vedere che, pe
- Page 307 and 308:
— 293 — finito dei due piani si
- Page 309 and 310:
— 295 — se vi è un terzo punto
- Page 311 and 312:
— 297 — questa forma, vi sarà
- Page 313 and 314:
l — 299 — Se poi di una retta a
- Page 315 and 316:
i — 301 — *' ed j, generalmente
- Page 317 and 318:
i — 303 — e) Se finalmente il c
- Page 319 and 320:
l — 305 — trova che le coordina
- Page 321 and 322:
i — 307 — reale), q^ = q^, giac
- Page 323 and 324:
i — 309 — * 185. Uguaglianza fr
- Page 325 and 326:
i — 311 — come uniti tutti i pu
- Page 327 and 328:
l — 313 — 17) Due piani simili
- Page 329 and 330:
— 315 — tutti per uno stesso pu
- Page 331 and 332:
\ — 317 — Per rappresentare ana
- Page 333 and 334:
— 319 — nate della retta p', ch
- Page 335 and 336:
— 321 — e perchè noi supponiam
- Page 337 and 338:
— 323 — dremo nella teoria dell
- Page 339 and 340:
— 325 — tuirà V inviluppo coni
- Page 341 and 342:
— 327 — 7) Sopra ogni retta di
- Page 343 and 344:
— 329 — 3) Introdotta sul princ
- Page 345 and 346:
— 331 — curva x^ -\- y'^ = 0; c
- Page 347 and 348:
— 333 — La prima definisce il p
- Page 349 and 350:
— 335 — nel campo proiettivo ;
- Page 351 and 352:
dove f{x, y, 0), f{x', — 337 —
- Page 353 and 354:
— 339 — 1) Si formino le deriva
- Page 355 and 356:
— 341 — l'equazione della tange
- Page 357 and 358:
(7) A = — 343 — l'altro dalla r
- Page 359 and 360:
— 345 — 304. Metodo delle polar
- Page 361 and 362:
— 347 — F (u^ V, w), come la co
- Page 363 and 364:
— 349 b) Le intersezioni di una c
- Page 365 and 366:
— 351 — e sega pure il secondo
- Page 367 and 368:
— 353 — dai quali si conducano
- Page 369 and 370:
— 355 — e si noti che, quando M
- Page 371 and 372:
I — 357 — zioni della retta VP
- Page 373 and 374:
— 359 — a primo grado, si ricon
- Page 375 and 376:
— 361 — in punti coincidenti da
- Page 377 and 378:
— 363 — gli ortocentri dei quat
- Page 379 and 380:
— 365 — 32) Dal teorema dell' e
- Page 381 and 382:
i — 367 — a, 6' le tangenti in
- Page 383 and 384:
— 369 — Queste proposizioni, di
- Page 385 and 386:
— 371 — Segando il primo fascio
- Page 387 and 388:
— 373 — done noti due punti: M
- Page 389 and 390:
— 376 — gente ad una iperbole c
- Page 391 and 392:
Le infinite coniche circo- scritte
- Page 393 and 394:
— 379 — una conica è iscritta
- Page 395 and 396:
— 381 — reale e distinta da que
- Page 397 and 398:
— 383 — tre coniche degenen (a
- Page 399 and 400:
— 385 — Se ora si suppone che d
- Page 401 and 402:
— 387 — colare alla tangente),
- Page 403 and 404:
— 389 — 7) Determinata una coni
- Page 405 and 406:
— 391 — Im- sicché ± Vx^ -\-
- Page 407 and 408:
— 393 — è tangente a K) i}). (
- Page 409 and 410:
— 395 — dove À, fi. V sono par
- Page 411 and 412:
— 397 — Partendo dall' equazion
- Page 413 and 414:
— 399 — La costruzione degli as
- Page 415 and 416:
— 401 — La prima proposizione s
- Page 417 and 418:
— 403 — gonali^ proponiamoci di
- Page 419 and 420:
— 405 — 7) Dati in grandezza e
- Page 421 and 422:
— 407 — 25) Ad una schiera di c
- Page 423 and 424:
— 409 — dovrà la (d) mancare d
- Page 425 and 426:
— 411 — II) Se nella (2) faccia
- Page 427 and 428:
— 413 — 244. Alcune formole rel
- Page 429 and 430:
— 415 — dove p è una costante
- Page 431 and 432:
— 417 — nelle (a), basterà far
- Page 433 and 434:
— 419 — caso. Ma si può chiede
- Page 435 and 436:
— 421 — Un terzo invariante si
- Page 437 and 438:
— 423 — dunque: nel passaggio d
- Page 439 and 440:
— 425 — nelle quali le incognit
- Page 441 and 442:
— 427 — 252. Teoremi di Apollon
- Page 443 and 444:
— 429 — 3) Scrivere l' equazion
- Page 445 and 446:
— 431 — 17) Dati sulla conica A
- Page 447 and 448:
— 433 — diagonale PQ; queste pe
- Page 449 and 450:
— 435 — Capitolo V. Proprietà
- Page 451 and 452:
— 437 — la involuzione dunque
- Page 453 and 454:
— 439 — Ciò premesso, assumiam
- Page 455 and 456:
— 441 — Per enunciare il risult
- Page 457 and 458:
— 443 — è indipendente dalla c
- Page 459 and 460:
- e\c -j- Q cos f) = —
- Page 461 and 462:
— 447 — lori costanti, coordina
- Page 463 and 464:
— 449 — rette formanti fascio c
- Page 465 and 466:
I — 451 — dei segmenti cosi ott
- Page 467 and 468:
— 453 — 38) Da questo teorema e
- Page 469 and 470:
— 455 — Al contrario, le propri
- Page 471 and 472:
— 457 — il piano di K' intorno
- Page 473 and 474:
— 459 — quella affinità che tr
- Page 475 and 476:
— 461 — sono paralleli agli asi
- Page 477 and 478:
— 463 — 12) n prodotto di due a
- Page 479:
— 465 — parallela alla retta P,
- Page 482 and 483:
— 468 — rebbe quando fosse rich
- Page 484 and 485:
- 470 — dove si suppone precisame
- Page 486 and 487:
— 472 — sistema di coordinate p
- Page 488 and 489:
— 474 — In modo perfettamente a
- Page 490 and 491: — 476 — comprenderà ora a prio
- Page 492 and 493: — 478 — punti dati, si possa co
- Page 494 and 495: — 480 — blema mostreremo tra po
- Page 496 and 497: — 482 — II. Sia data una riga a
- Page 498 and 499: ^ 484 — dove p, q possono riguard
- Page 500 and 501: — 486 — sarà noto a priori (ca
- Page 502 and 503: — 488 — angoli particolari che
- Page 504 and 505: — 490 — 278. Il problema della
- Page 506 and 507: — 492 — 6) Retta generica del f
- Page 508 and 509: — 494 — 21) Condizioni perchè
- Page 511 and 512: G. CASTELNUOVO Professore all' Univ
- Page 515 and 516: 497 — Parte Quarta. Geometria ana
- Page 517 and 518: — 499 — e la terza coordinata {
- Page 519 and 520: — 501 — Indicando i tre denomin
- Page 521 and 522: — 503 — Viceversa : ogni equazi
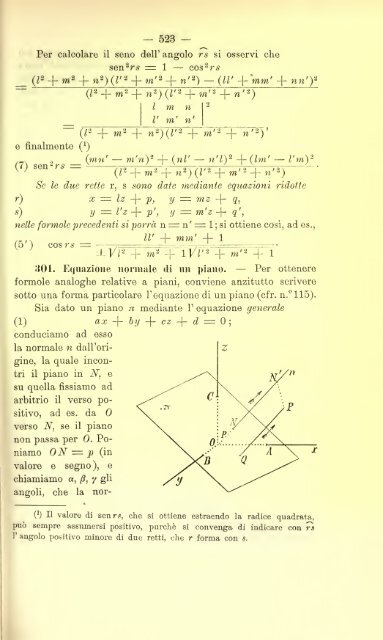
- Page 523 and 524: — 505 — 287. Condizione di para
- Page 525 and 526: (!') — 507 — 289. Equazioni di
- Page 527 and 528: — 509 — se invece sta sopra xy^
- Page 529 and 530: — 511 — Questa rappresenta un p
- Page 531 and 532: — 513 — allora, od esiste un si
- Page 533 and 534: — 515 — punto (2, — 1, 1) e p
- Page 535 and 536: — 517 — spezzate aventi gli ste
- Page 537 and 538: — 519 — 297. Distanza dì due p
- Page 539: e quindi , 'cosxr = — , — 521
- Page 543 and 544: — 525 — Ora questi risultati, e
- Page 545 and 546: — 527 — Similmente si vede che
- Page 547 and 548: — 629 — quarto vertice dalla fa
- Page 549 and 550: — 531 — ordine uguagliato a zer
- Page 551 and 552: — 533 — perpendicolare. (Es. nu
- Page 553 and 554: — 535 — di geometria elementare
- Page 555 and 556: — 537 — menti dei vettori dati,
- Page 557 and 558: — 539 — Si osserverà che i nov
- Page 559 and 560: — 541 — cartesiano^ le coordina
- Page 561 and 562: ^ — 543 — d' = zZ, mediante la
- Page 563 and 564: — 545 — togliere, introducendo
- Page 565 and 566: — 547 — genee, giova tuttavia t
- Page 567 and 568: — 549 — piani P; riguardata sot
- Page 569 and 570: — 551 — Si ha qui una giustific
- Page 571 and 572: — 553 — dinate (1, 1, 1, 1). Be
- Page 573 and 574: — 555 — dove i k l m B una qual
- Page 575 and 576: — 557 — Per costruire un punto
- Page 577 and 578: — 559 — che si possa dedurre co
- Page 579 and 580: — 561 — Il teorema si dimostra
- Page 581 and 582: — 563 — come piano XY di un nuo
- Page 583 and 584: — 565 — II. — 10) Trovare 1'
- Page 585 and 586: — 667 — essere tutte nulle). Al
- Page 587 and 588: — 569 — D' altra parte è spess
- Page 589 and 590: X — a
- Page 591 and 592:
— 573 — Se il vertice coincide
- Page 593 and 594:
— ; 576 — equidistanti dal punt
- Page 595 and 596:
— 577 — essi (n.° 312). Tra gl
- Page 597 and 598:
— 579 — dello spazio mediante u
- Page 599 and 600:
— 581 — quel modo, pur di scegl
- Page 601 and 602:
-^ 583 — glianze (1). Si conclude
- Page 603 and 604:
— 585 — una posizione assunta d
- Page 605 and 606:
— 587 — uniti, ed i cui spigoli
- Page 607 and 608:
— 589 — piani corrispondenti, s
- Page 609 and 610:
— 591 — Finalmente se, dato un
- Page 611 and 612:
ci fornisce A: = zioni (7), ci dà
- Page 613 and 614:
— 595 — 839. Polarità nello sp
- Page 615 and 616:
— 597 — Esercizi. I. — 1) Una
- Page 617 and 618:
— 599 — si osservi che le condi
- Page 619 and 620:
— 601 — 18) Assunto r asse di u
- Page 621 and 622:
— 603 — (n.*' 323), r ellissoid
- Page 623 and 624:
— 605 — La curva intersezione d
- Page 625 and 626:
— 607 — punto comune alle due r
- Page 627 and 628:
— 609 — 345. Per costruire il p
- Page 629 and 630:
— 611 — P', mentre il coefficie
- Page 631 and 632:
— 613 — quazione del piano tang
- Page 633 and 634:
— 615 — questa ipotesi sarà so
- Page 635 and 636:
— 617 — Due rette siffatte, in
- Page 637 and 638:
— 619 — quadrica in un punto R
- Page 639 and 640:
— 621 — una quadrica : due pian
- Page 641 and 642:
— 623 — esso pure alla quadrica
- Page 643 and 644:
— 625 — p' ed ì piani n' della
- Page 645 and 646:
— 627 — zioni lineari fra i coe
- Page 647 and 648:
— 629 — goli collo stesso verti
- Page 649 and 650:
— 631 — cano in P la quadrica,
- Page 651 and 652:
— 633 — Cosi continuando, vedia
- Page 653 and 654:
— 635 — Segue inoltre che il pr
- Page 655 and 656:
— 637 — Dualmente, se i sostegn
- Page 657 and 658:
— 639 — Esse passano tutte per
- Page 659 and 660:
— 641 — g) / vertici dei quattr
- Page 661 and 662:
— 643 — autoconiugato rispetto
- Page 663 and 664:
— 645 — lungo coniche, che hann
- Page 665 and 666:
— 647 — (Cfr. n." 231, es. 9),
- Page 667 and 668:
— 649 — %• 1 (^))> o può non
- Page 669 and 670:
— 651 — che si riconosce essere
- Page 671 and 672:
— 653 — di centro, i paraboloid
- Page 673 and 674:
— 655 — 2^0 ) della quadrica (n
- Page 675 and 676:
— 657 — triangolo, insieme al c
- Page 677 and 678:
— 659 — Concludiamo che una qua
- Page 679 and 680:
— 661 — del n.° 378^ la quale
- Page 681 and 682:
k — 663 — Ritornando al problem
- Page 683 and 684:
— 665 — drangolo ; ed è autopo
- Page 685 and 686:
— 667 — 4) Date le equazioni di
- Page 687 and 688:
— 669 - a) Supposto anzitutto che
- Page 689 and 690:
— 671 — rappresentante un cono
- Page 691 and 692:
— 673 — mentre k cresce in valo
- Page 693 and 694:
— 675 — Il piano y =: iavece se
- Page 695 and 696:
— 677 — 387. Iperboloide a due
- Page 697 and 698:
— 679 — il piano polare di ques
- Page 699 and 700:
— 681 — mente che la quarta coo
- Page 701 and 702:
questa, colla traslazione di assi a
- Page 703 and 704:
— 685 — Per procurarci le equaz
- Page 705 and 706:
— 687 — (2) a'nX^ H h 2«^',,XF
- Page 707 and 708:
— 689 — Se invece avessimo adop
- Page 709 and 710:
— 691 — Osservazione. — Abbia
- Page 711 and 712:
Le ultime due ci danno — 693 —
- Page 713 and 714:
— 695 — sicché il paraboloide
- Page 715 and 716:
— 697 — Ora questo teorema può
- Page 717 and 718:
— 699 — 2) Ogni iperboloide rif
- Page 719 and 720:
— 701 — dri siffatti» (cfr. n.
- Page 721 and 722:
— 703 — perfide. Ora, se -ST è
- Page 723 and 724:
— 705 — quattro fasci impropri
- Page 725 and 726:
— 707 — centro dell'ellissoide.
- Page 727 and 728:
— 709 — come risulta dall' Oss.
- Page 729 and 730:
— 711 — sopra una stessa retta,
- Page 731 and 732:
— 713 — cono dette direzioni as
- Page 733 and 734:
— 715 — Ora sappiamo che un con
- Page 735 and 736:
— 717 — una quadrica inviluppo
- Page 737 and 738:
— 719 — si trovano distribuiti
- Page 739 and 740:
— 721 — per la direttrice /'. l
- Page 741:
— 723 — due punti fissi della i
- Page 744 and 745:
— 726 — 6) Condizione, perchè
- Page 746 and 747:
(22) A (23) — 728 — 22) Area de
- Page 748 and 749:
— 730 — 35) Condizioni, perchè
- Page 751 and 752:
INDICE Prefazione pag. INTRODUZIONE
- Page 753 and 754:
— 735 — 41. Sistema delle coord
- Page 755 and 756:
— 737 — 91. Coppia comune a due
- Page 757 and 758:
— 739 — 145. Concetto generale
- Page 759 and 760:
— 741 — 197. Intersezioni di un
- Page 761 and 762:
— 743 — Cap. V. Proprietà foca
- Page 763 and 764:
— 745 — 300. Angolo di due rett
- Page 765 and 766:
— 747 — 362. Quadriche a punti
- Page 772 and 773:
Kt 1 UKIN Astronomy/Mathematics/Sta