30845 Suppl Giot.pdf - Giornale Italiano di Ortopedia e Traumatologia
30845 Suppl Giot.pdf - Giornale Italiano di Ortopedia e Traumatologia
30845 Suppl Giot.pdf - Giornale Italiano di Ortopedia e Traumatologia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Durable cure and reconstructive success in osteogenic sarcoma<br />
Cura durevole e successo ricostruttivo nel sarcoma osteogenico<br />
J.H. Healey<br />
The lament that osteogenic sarcoma<br />
(OGS) treatment has improved little<br />
since work of Rosen in cytotoxic<br />
chemotherapy and Campanacci and<br />
Marcove in limb salvage is common,<br />
but inaccurate 1-3 . This paper reviews<br />
the progress in chemotherapy, highlights<br />
basic science advances that may<br />
change treatment, and introduces new<br />
prosthetic measures that will make<br />
joint reconstruction more durable.<br />
Progress in these realms promise to<br />
transform OGS care.<br />
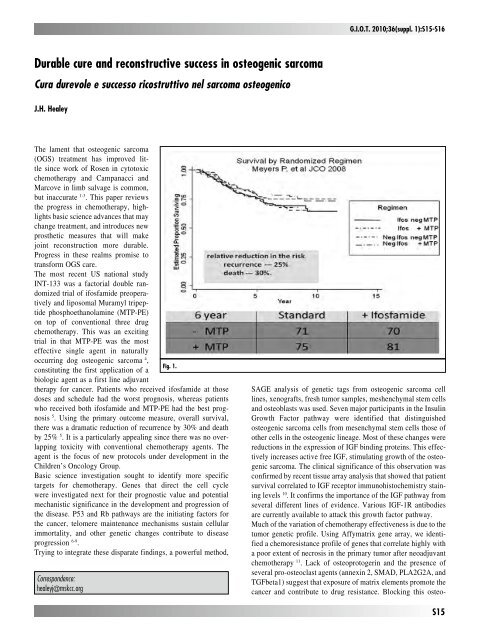
The most recent US national study<br />
INT-133 was a factorial double randomized<br />
trial of ifosfamide preoperatively<br />
and liposomal Muramyl tripeptide<br />
phosphoethanolamine (MTP-PE)<br />
on top of conventional three drug<br />
chemotherapy. This was an exciting<br />
trial in that MTP-PE was the most<br />
effective single agent in naturally<br />
occurring dog osteogenic sarcoma 4 ,<br />
constituting the first application of a<br />
biologic agent as a first line adjuvant<br />
therapy for cancer. Patients who received ifosfamide at those<br />
doses and schedule had the worst prognosis, whereas patients<br />
who received both ifosfamide and MTP-PE had the best prognosis<br />
5 . Using the primary outcome measure, overall survival,<br />
there was a dramatic reduction of recurrence by 30% and death<br />
by 25% 5 . It is a particularly appealing since there was no overlapping<br />
toxicity with conventional chemotherapy agents. The<br />
agent is the focus of new protocols under development in the<br />
Children’s Oncology Group.<br />
Basic science investigation sought to identify more specific<br />
targets for chemotherapy. Genes that <strong>di</strong>rect the cell cycle<br />
were investigated next for their prognostic value and potential<br />
mechanistic significance in the development and progression of<br />
the <strong>di</strong>sease. P53 and Rb pathways are the initiating factors for<br />
the cancer, telomere maintenance mechanisms sustain cellular<br />
immortality, and other genetic changes contribute to <strong>di</strong>sease<br />
progression 6-9 Fig. 1.<br />
.<br />
Trying to integrate these <strong>di</strong>sparate fin<strong>di</strong>ngs, a powerful method,<br />
Correspondence:<br />
healeyj@mskcc.org<br />
G.I.O.T. 2010;36(suppl. 1):S15-S16<br />
SAGE analysis of genetic tags from osteogenic sarcoma cell<br />
lines, xenografts, fresh tumor samples, meshenchymal stem cells<br />
and osteoblasts was used. Seven major participants in the Insulin<br />
Growth Factor pathway were identified that <strong>di</strong>stinguished<br />
osteogenic sarcoma cells from mesenchymal stem cells those of<br />
other cells in the osteogenic lineage. Most of these changes were<br />
reductions in the expression of IGF bin<strong>di</strong>ng proteins. This effectively<br />
increases active free IGF, stimulating growth of the osteogenic<br />
sarcoma. The clinical significance of this observation was<br />
confirmed by recent tissue array analysis that showed that patient<br />
survival correlated to IGF receptor immunohistochemistry staining<br />
levels 10 . It confirms the importance of the IGF pathway from<br />
several <strong>di</strong>fferent lines of evidence. Various IGF-1R antibo<strong>di</strong>es<br />
are currently available to attack this growth factor pathway.<br />
Much of the variation of chemotherapy effectiveness is due to the<br />
tumor genetic profile. Using Affymatrix gene array, we identified<br />
a chemoresistance profile of genes that correlate highly with<br />
a poor extent of necrosis in the primary tumor after neoadjuvant<br />
chemotherapy 11 . Lack of osteoprotogerin and the presence of<br />
several pro-osteoclast agents (annexin 2, SMAD, PLA2G2A, and<br />
TGFbeta1) suggest that exposure of matrix elements promote the<br />
cancer and contribute to drug resistance. Blocking this osteo-<br />
S15