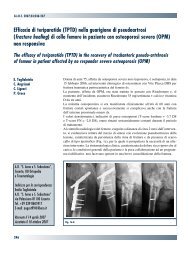
30845 Suppl Giot.pdf - Giornale Italiano di Ortopedia e Traumatologia
30845 Suppl Giot.pdf - Giornale Italiano di Ortopedia e Traumatologia
30845 Suppl Giot.pdf - Giornale Italiano di Ortopedia e Traumatologia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
G.I.O.T. 2010;36(suppl. 1):S270-S272<br />
Matematizzazione <strong>di</strong> un’osteotomia <strong>di</strong>stale: applicazione dell’Osteogoniometro (OGr)<br />
nell’alluce valgo e nell’alluce rigido<br />
F. Cancilleri, P. ronconi * , N. Martinelli, a. Marinozzi<br />
rIaSSuNTO<br />
Le osteotomie <strong>di</strong>stali sono procedure sicure e affidabili per la<br />
correzione chirurgica dell’alluce valgo. Queste procedure hanno<br />
lo scopo <strong>di</strong> spostare la prima testa metatarsale lateralmente più<br />
vicino alla sua posizione normale, restaurando una normale geometria<br />
del primo raggio. Tuttavia la valutazione ad “occhio nudo”<br />
dello spostamento, può essere improprio con possibile sviluppo <strong>di</strong><br />
complicanze 1 . Un approccio matematico alle osteotomie permette<br />
<strong>di</strong> valutare pre-operatoriamente gli angoli <strong>di</strong> taglio, garantendo<br />
spostamenti del metatarso con maggiore precisione.<br />
Parole chiave: osteotomia <strong>di</strong>stale, osteogoniometro, alluce valgo.<br />
SuMMary<br />
Distal osteotomies for hallux valgus surgery are safe and reliable<br />
procedures. These procedures aim to move more laterally the first<br />
metatarsal head in a more physiologic position, restoring a normal<br />
geometry of the first ray. However, assessment of lateral translation<br />
entity could be inaccurate, with possible onset of complications 1 . A<br />
mathematical approach to <strong>di</strong>stal osteotomy allows to evaluate preoperatively<br />
the cut-angles, ensuring lateral translations of the metatarsal<br />
with more precision. Uniplanar 2 or multiplanar osteotomies 3<br />
4 should be made considering the following values: a) translation of<br />
the metatarsal head: the mathematical formula to calculate it is sp =<br />
2ac(senγ/2) (Fig. 1). b) Shortening of the metatarsal head should be<br />
calculate accor<strong>di</strong>ng to the arch theory with the formula: Arr = r-(rcos<br />
α) (Fig. 2). c) plantar translation of the metatarsal head: should be at<br />
least the double of the shortening. In order to simplify the count of<br />
the angle values we have realized a conversion table where plantar<br />
translation and shortening values, in degrees, are reported on the<br />
or<strong>di</strong>nates axis in correlation to the lateral translation values reported<br />
on the abscissa axis (Fig. 3). The practical application of what has<br />
been calculated on the ra<strong>di</strong>ographs has been simplified by the use<br />
of a new device, called osteogoniometry (OGR), that ensures reliability<br />
of the calculated values 1 . In a comparative study between<br />
two groups of patients treated for hallux valgus with either biplanar<br />
osteotomy performed with a free hand technique or triplanar osteotomy<br />
performed wit the OGR, a statistically significant decrease in<br />
Università Campus Bio Me<strong>di</strong>co <strong>di</strong> Roma, Malattie dell’Apparato Locomotore; 2 Foot<br />
Me<strong>di</strong>cal Hospital <strong>di</strong> Roma<br />
In<strong>di</strong>rizzo per la corrispondenza:<br />
Francesco Cancilleri. E-mail: f.cancilleri@unicampus.it<br />
S270<br />
the onset of metatarsalgia has been detected in the group treated with<br />
triplanar osteotomy performed with the OGR 5 . The use of the OGR<br />
allows to achieve more precision of the osteotomy cuts accor<strong>di</strong>ng to<br />
the pre-operative planning.<br />
Key words: <strong>di</strong>stal osteotomy, bone goniometry, hallux valgus<br />
INTrODuzIONE<br />
L’evoluzione delle osteotomie e la loro maggiore complessità<br />
nella realizzazione pone la necessità da parte del chirurgo <strong>di</strong><br />
uno stu<strong>di</strong>o matematico per definirne l’angolo <strong>di</strong> taglio garantendo<br />
con precisione gli spostamenti del metatarso effettuati<br />
con sezioni alla base, alla <strong>di</strong>afisi o alla testa. Il trasferimento sul<br />
campo operatorio <strong>di</strong> quanto calcolato sui ra<strong>di</strong>ogrammi, realizzati<br />
a <strong>di</strong>stanza focale predefinita in rapporto 1/1, è possibile con<br />
l’utilizzo <strong>di</strong> un adeguato apparecchio denominato OGR 1 . Ciò<br />
rappresenta una guida nella pratica chirurgica e consente una più<br />
facile riproducibilità.<br />
MaTErIaLI E METODI<br />
Le osteotomie monoplanari 2 o multiplanari 3 4 devono essere<br />
effettuate considerando i seguenti valori: a) spostamento della<br />
testa metatarsale: la formula matematica per calcolarlo è sp =<br />
2ac(senγ/2) (Fig. 1); b) arretramento della testa metatarsale calcolato<br />
secondo la teoria dell’arco, la cui formula è Arr = r-(rcos α)<br />
(Fig. 2); c) abbassamento della testa metatarsale: solitamente deve<br />
essere almeno il doppio del valore dell’arretramento. Per semplificare<br />
i conteggi dei valori fin qui esposti abbiamo realizzato una<br />
tavola <strong>di</strong> conversione dove sulle or<strong>di</strong>nate vi sono i valori in gra<strong>di</strong><br />
dell’abbassamento e dell’arretramento in rapporto ai valori <strong>di</strong><br />
spostamento riportati sulle ascisse (Fig. 3). L’applicazione pratica<br />
<strong>di</strong> quanto calcolato sui ra<strong>di</strong>ogrammi, è possibile con l’utilizzo<br />
<strong>di</strong> un adeguato apparecchio denominato OGR, garantendo la<br />
riproducibilità dei valori calcolati 1 . Nello stu<strong>di</strong>o eseguito su due<br />
gruppi <strong>di</strong> osteotomie biplanari versus triplanari abbiamo rilevato<br />
un valore statisticamente significativo <strong>di</strong> minore incidenza <strong>di</strong><br />
metatarsalgia da trasferimento nel gruppo delle triplanari realizzate<br />
con l’uso dell’OGR 5 . L’impiego dell’OGR consente una<br />
maggiore precisione nell’esecuzione dell’osteotomia rispetto ai<br />
valori calcolati pre-operatoriamente.<br />
Le osteotomie <strong>di</strong>stali tipo Austin 2 , Kalish, Rever<strong>di</strong>n ecc. e <strong>di</strong>afisarie<br />
tipo “scarf”, sono tagli angolati che possono variare dai 60°<br />
ai 90° a livello della testa del I metatarsale o con doppio angolo<br />
per le “scarf”, possono essere eseguite inserendo un filo guida. Gli<br />
spostamenti che si ottengono in rapporto all’inserimento del filo