- Page 1 and 2:
UNIVERSIDADE DE SÃO PAULO ESCOLA D
- Page 4 and 5:
Dedico esse trabalho carinhosamente
- Page 6 and 7:
Aos queridos Guilherme, Damiana, Va
- Page 8 and 9:
Resumo LEONEL, E.D. Modelos Não Li
- Page 10 and 11:
Sumário 1. - Introdução.........
- Page 12 and 13:
6.1 - Formulações do MEC para a A
- Page 14 and 15:
9.2.3 - 3° Cenário...............
- Page 16 and 17:
1. - Introdução 1.1 - Objetivos e
- Page 18 and 19:
métodos numéricos de tal maneira
- Page 20 and 21:
A formulação do MEC para o proble
- Page 22 and 23:
2. - Revisão Bibliográfica Aprese
- Page 24 and 25:
variações lineares, quadráticas
- Page 26 and 27:
Um dos primeiros trabalhos que trat
- Page 28 and 29:
zona de processo, ocorre a perda de
- Page 30 and 31:
ANG & AMIN (1968) descrevem os conc
- Page 32 and 33:
entre os graus de liberdade do elem
- Page 34 and 35:
e SORM na análise de confiabilidad
- Page 36 and 37:
modelo mecânico um modelo de dano.
- Page 38 and 39:
atuante devido a presença de uma r
- Page 40 and 41:
programação matemática. Apesar d
- Page 42 and 43:
Além de alguns dos trabalhos já c
- Page 44 and 45:
3. - Mecânica da Fratura e Contato
- Page 46 and 47:
superfície e Ω é o domínio do
- Page 48 and 49:
Na teoria proposta pela mecânica d
- Page 50 and 51:
de intensidade de tensão depende t
- Page 52 and 53:
O trabalho de PEREIRA (2004) aborda
- Page 54 and 55:
1 ⎛ θ ⎞ τ rθ = ⋅cos ⎜
- Page 56 and 57:
em uma direção arbitrária. No tr
- Page 58 and 59:
apresenta dimensões grandes se com
- Page 60 and 61:
de dissipação de energia e obter
- Page 62 and 63:
Figura 3.7 Distribuição de tensõ
- Page 64 and 65:
principal 2) A fissura cresce perpe
- Page 66 and 67:
3.11 - Fadiga dos Materiais f t σ
- Page 68 and 69:
e uma vida útil, correspondendo a
- Page 70 and 71:
empregados para inspeção podem se
- Page 72 and 73:
Figura 3.15 Definição de K , max
- Page 74 and 75:
Apesar de ser um critério muito ut
- Page 76 and 77:
do material. Em materiais de compor
- Page 78 and 79:
contato, exceder a soma entre a coe
- Page 80 and 81:
4. - Tópicos de Confiabilidade Est
- Page 82 and 83:
efeitos e à resistência ou rigide
- Page 84 and 85:
distribuição qualquer. Nesse caso
- Page 86 and 87:
Dessa forma, com a utilização dos
- Page 88 and 89:
aproximações quadráticas dispon
- Page 90 and 91:
Independente do método utilizado p
- Page 92 and 93:
literatura há uma grande busca por
- Page 94 and 95:
comportamento mecânico da estrutur
- Page 96 and 97:
Figura 4.6 Sistema adaptativo para
- Page 98 and 99:
Assim determina-se a superfície de
- Page 100 and 101:
um efeito mecânico, térmico, magn
- Page 102 and 103:
alguns dias, pela despassivação d
- Page 104 and 105:
modelos de degradação. A formula
- Page 106 and 107:
5. - Método dos Elementos de Conto
- Page 108 and 109:
A solução da Eq. (5.2) representa
- Page 110 and 111:
Nesse ponto deve-se empregar a equa
- Page 112 and 113:
A singularidade forte, 1 r , da sol
- Page 114 and 115:
De acordo com o grau de aproximaç
- Page 116 and 117:
5.5 - Construção do Sistema de Eq
- Page 118 and 119:
* * * pi ⎪⎧ 2⋅ µ ⋅υ ∂u
- Page 120 and 121:
é descrita empregando-se a equaç
- Page 122 and 123:
Já o último termo do segundo memb
- Page 124 and 125:
espeitada com o ponto fonte interna
- Page 126 and 127:
especiais devem ser efetuadas a res
- Page 128 and 129:
6. - Formulações Não Lineares do
- Page 130 and 131:
pontos internos presente em cada um
- Page 132 and 133:
código computacional desenvolvido.
- Page 134 and 135:
p x p x ⎡U ⎤ ⎡ Cos( θ ) Sen(
- Page 136 and 137:
Nessa formulação foram considerad
- Page 138 and 139:
formulações utilizadas levam a re
- Page 140 and 141:
37,5 225 75 300 37,5 Capítulo 6 -
- Page 142 and 143:
6.1.8 - Exemplo 3: Viga Multi-Fissu
- Page 144 and 145:
comportamento da mecânica da fratu
- Page 146 and 147:
comprimento e 1 metro de altura, co
- Page 148 and 149:
duas fissuras, cada uma com comprim
- Page 150 and 151:
esquerda. O carregamento considerad
- Page 152 and 153:
emprega funções de Green. Na Fig.
- Page 154 and 155:
claramente a localização da danif
- Page 156 and 157:
egião do contato, uma vez que esta
- Page 158 and 159:
espostas obtidas usando os dois mé
- Page 160 and 161:
espostas obtidas por ambos os model
- Page 162 and 163:
deslocamento X quando se compara es
- Page 164 and 165:
Como na formulação serão conside
- Page 166 and 167:
p n k k k Ndn Nic ⎡ Ndc Ndc Ndc
- Page 168 and 169:
programa ANSYS, onde um modelo equi
- Page 170 and 171:
Tensão XY (kN/m 2 ) -5,00E+04 0 0,
- Page 172 and 173:
comparativo dos deslocamentos x. Po
- Page 174 and 175:
comportamento do escorregamento ent
- Page 176 and 177:
Deslocamento Y (m) 0,0005 -0,0005 -
- Page 178 and 179:
horário até seu canto superior es
- Page 180 and 181:
7. - Acoplamento entre Método dos
- Page 182 and 183:
elemento da Fig. (7.1) são obtidas
- Page 184 and 185:
domínio, como uma linha de carga,
- Page 186 and 187:
O esquema da Fig (7.3) estende-se,
- Page 188 and 189:
permite a análise de fibras que fo
- Page 190 and 191:
Serão agora descritos os três pro
- Page 192 and 193:
compostas por 50, 100 e 200 element
- Page 194 and 195:
pode ser entendido como uma concent
- Page 196 and 197:
quadrados nas equações de desloca
- Page 198 and 199:
A figura acima mostra também a efi
- Page 200 and 201:
Deslocamento Contorno X (m) 0,00004
- Page 202 and 203:
0,40 y 0,20 0,25 0,25 0,25 0,25 0,2
- Page 204 and 205:
De acordo com os diagramas comparat
- Page 206 and 207:
finitos. Inicialmente será apresen
- Page 208 and 209:
Limite Elástico Inicial Deformaç
- Page 210 and 211:
plástica, plástico. Substituindo
- Page 212 and 213:
. . p p Capítulo 7 - Acoplamento e
- Page 214 and 215:
sendo ( σ ) . sign − q ⋅ E .
- Page 216 and 217:
Deslocamento Contorno X (m) 0,060 0
- Page 218 and 219:
imposto em sua extremidade direita,
- Page 220 and 221:
Deformação Plástica 2,08E-02 2,0
- Page 222 and 223:
0,05 0,40 y 0,20 0,25 0,25 0,25 0,2
- Page 224 and 225:
Deformação Elástica 0,003 0,002
- Page 226 and 227:
Força Normal (kN) 25,000 20,000 15
- Page 228 and 229:
ensaio de tração. A rigidez dos e
- Page 230 and 231:
conforme apresenta a Eq. (7.4), con
- Page 232 and 233:
Na Fig. (7.61) estão apresentadas
- Page 234 and 235:
Figura 7.64 Crescimento da fissura.
- Page 236 and 237:
enrijecedores posicionados no inter
- Page 238 and 239:
egiões próximas as fissuras. No p
- Page 240 and 241:
enrijecedores. A diferença se faz
- Page 242 and 243:
-1E-005 -3E-005 Capítulo 7 - Acopl
- Page 244 and 245:
na Fig. (7.83). As propriedades dos
- Page 246 and 247:
8. - Modelo de Fadiga para Metais e
- Page 248 and 249: Vale ressaltar que o procedimento d
- Page 250 and 251: k 90,0 80,0 70,0 60,0 50,0 40,0 30,
- Page 252 and 253: Comprimento da Fissura 5,5 5 4,5 4
- Page 254 and 255: A estrutura foi analisada e a confi
- Page 256 and 257: Figura 8.13 Trajetória de crescime
- Page 258 and 259: alcança o comprimento de 0,60 m. A
- Page 260 and 261: 8.6 - Exemplo 5: Chapa com Múltipl
- Page 262 and 263: Fator de Intensidade de Tensão Equ
- Page 264 and 265: 9. - Acoplamento entre Modelos Mec
- Page 266 and 267: sendo: P R a força de superfície
- Page 268 and 269: necessita de um número maior de co
- Page 270 and 271: considerada como variável determin
- Page 272 and 273: intensidade de tensão em função
- Page 274 and 275: obtidas pelos quatro métodos de co
- Page 276 and 277: permite análises de confiabilidade
- Page 278 and 279: vista de condições de contorno co
- Page 280 and 281: carregamento atuante ~ ( 5,0;0,50 )
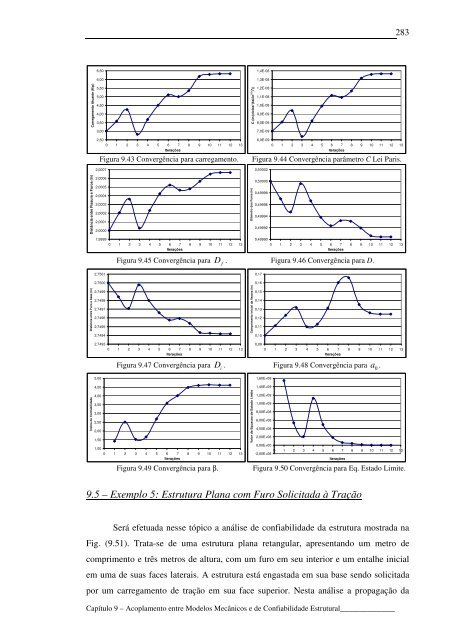
- Page 282 and 283: ponto de projeto é feito avaliando
- Page 284 and 285: Por meio dessa figura pode-se obser
- Page 286 and 287: progressiva quanto após convergên
- Page 288 and 289: 9.4 - Exemplo 4: Estrutura Plana Co
- Page 290 and 291: finalmente o parâmetro C da lei de
- Page 292 and 293: permanece sendo a apresentada na Eq
- Page 294 and 295: ser atribuídas, em parte, à const
- Page 296 and 297: nas análises anteriores constata-s
- Page 300 and 301: do problema. Através do MSR a estr
- Page 302 and 303: do modelo mecânico. Os modelos MSR
- Page 304 and 305: Os resultados ilustrados nessas fig
- Page 306 and 307: Os resultados ilustrados nessas fig
- Page 308 and 309: modelo mecânico durante cada itera
- Page 310 and 311: Na análise de confiabilidade a equ
- Page 312 and 313: aleatórias. Foram consideradas as
- Page 314 and 315: 10. - Acoplamento entre Modelo Meca
- Page 316 and 317: Esse conjunto de métodos foi popul
- Page 318 and 319: ponto ( , ) E a matriz hessiana em
- Page 320 and 321: k + 1 k λ = v . k ( ) ( ) t k k W
- Page 322 and 323: sendo que: Capítulo 10 - Acoplamen
- Page 324 and 325: Nesse modelo os estados limites sã
- Page 326 and 327: valor. Nesse instante a estrutura s
- Page 328 and 329: Foram adotadas as seguintes proprie
- Page 330 and 331: significativo. Esse valor aumenta a
- Page 332 and 333: lei de Paris n = 2,70 . A lei de Pa
- Page 334 and 335: estrição quanto a dimensão míni
- Page 336 and 337: Os parâmetros de custo envolvidos
- Page 338 and 339: confiabilidade, assim, nessa análi
- Page 340 and 341: 11. - Considerações Finais Este t
- Page 342 and 343: BOTTA (2003). No entanto, os modelo
- Page 344 and 345: 12. - Referências Bibliográficas
- Page 346 and 347: BAZANT, Z.P; LI, Y. N. (1995). Stab
- Page 348 and 349:
BUYUKOZTURK, O; HEARING, B. (1998).
- Page 350 and 351:
CRUSE, T. A. (1969). Numerical solu
- Page 352 and 353:
FERRO, N.C.P.; VENTURINI, W.S. (199
- Page 354 and 355:
HERTZ,H. (1882). On the contact of
- Page 356 and 357:
KRAJCINOVIC, D; MASTILOVIC,S. (2001
- Page 358 and 359:
MACIEL, D.N. (2003), Determinação
- Page 360 and 361:
MODEER,M. (1979). A Fracture Mechan
- Page 362 and 363:
PARIS, F; CAÑAS, J. (1997). Bounda
- Page 364 and 365:
RIBEIRO, G. O. (1992). Sobre a form
- Page 366 and 367:
SOARES, R.C. (2001). Um estudo sobr
- Page 368 and 369:
VIRKLER, D.A; HILLBERRY, B.M; GOEL,
- Page 370 and 371:
Anexo A. - Integrais Singulares De
- Page 372 and 373:
Matriz H H = C 1 12 1 H = −C ⋅(
- Page 374 and 375:
Anexo B. - Integrais Analíticas Hi
- Page 376 and 377:
{ ( ) 1 C6 3 S22 = ⋅ ⎡( C4 + 2
- Page 378 and 379:
Matriz D ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ) ( ) 2
- Page 380 and 381:
Matriz S ⎧ 1 ⎪⎡ ⎛ 1 ⎞⎤
- Page 382 and 383:
⎧⎪ ⎡ ⎛ 1 ⎞⎤ 1 ⎫⎪
- Page 384 and 385:
Anexo C. - Sub-Elementação Quando
- Page 386 and 387:
Figura C.2 Teste para verificar a n
- Page 388 and 389:
Anexo D. - O Concreto Estrutural O
- Page 390 and 391:
Comportamento do Concreto à Compre
- Page 392 and 393:
Comportamento do Concreto Sujeito a
- Page 394 and 395:
Anexo E. - Função Delta de Dirac
- Page 396 and 397:
Anexo F. - A Mecânica do Dano Dive
- Page 398 and 399:
Figura F.2 Representação variáve
- Page 400 and 401:
Anexo G. - Coeficientes Planos de E
- Page 402 and 403:
( 1 δ ) ( 1 δ ) ( 1 δ ) ⎡ x1 x
- Page 404 and 405:
( 1 δ ) ( 1 δ ) ⋅ ( 1+ Ψ ⋅δ
- Page 406 and 407:
( 1 δ ) ( 1 δ ) ( 1 δ ) ( 1 δ )
- Page 408 and 409:
Anexo H. - Método Golden Section N
- Page 410 and 411:
por 1 X e u X . Por outro lado, se
- Page 412 and 413:
Para o problema considerado o méto
- Page 414 and 415:
Anexo I. - Tópicos da Teoria da El
- Page 416 and 417:
I.2 - Relações Constitutivas Em e
- Page 418 and 419:
deslocamentos. A não linearidade d
- Page 420 and 421:
I.7 - Tensões Principais O estado