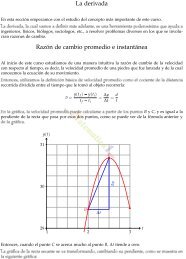
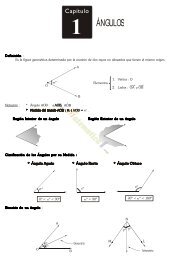
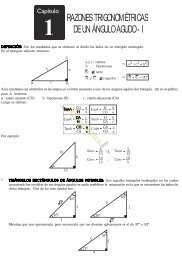
- Page 1 and 2:
INDICE GEOMETRIA ANALITICA PLANA CA
- Page 3 and 4:
INDICE XI Articulo Página 56. Ecua
- Page 5 and 6:
INDICE XIII CAPITULO XIV Articulo E
- Page 7 and 8:
CAPITULO PRIM ERO SISTEMAS DE COORD
- Page 9 and 10:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 3 En efecto
- Page 11 and 12:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 5 La distan
- Page 13 and 14:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS eje Y , med
- Page 15 and 16:
SISTEM AS DE COORDENADAS 9 3. Si A,
- Page 17 and 18:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 11 6. Dista
- Page 19 and 20:
SISTEM AS DE COORDENADAS 13 Por Geo
- Page 21 and 22:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 15 EJERCICI
- Page 23 and 24:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS D efinició
- Page 25 and 26:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 19 Ejemplo.
- Page 27 and 28:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 21 pendient
- Page 29 and 30:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 23 Recípro
- Page 31 and 32:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 25 10. Hall
- Page 33 and 34:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 27 todos lo
- Page 35 and 36:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 29 Por hip
- Page 37 and 38:
SISTEMAS DE COORDENADAS 31 CONDICIO
- Page 39 and 40:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 41 and 42:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 43 and 44:
GRAFICA DE U N A ECUACION Y LUGARES
- Page 45 and 46:
GRAFICA DE U N A ECUACION Y LUGARES
- Page 47 and 48:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 49 and 50:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 51 and 52:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 53 and 54:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 55 and 56:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 57 and 58:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 59 and 60:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 61 and 62:
GRAFICA DE UNA ECUACION Y LUGARES G
- Page 63 and 64:
LA LINEA RECTA 57 Pi (x i, yi) y P
- Page 65 and 66:
LA LINEA RECTA 59 f 27. Otras forma
- Page 67 and 68:
LA LINEA RECTA 61 2. Si se multipli
- Page 69 and 70:
LA LINEA RECTA 63 Ejemplo 2. Hallar
- Page 71 and 72:
LA LINEA RECTA 65 28. Las ecuacione
- Page 73 and 74:
LA LINEA RECTA 67 partir de una con
- Page 75 and 76:
También , por ser las pendientes i
- Page 77 and 78:
LA LINEA RECTA 71 10 . En ¡as ecua
- Page 79 and 80:
LA LINEA RECTA 73 Para las posicion
- Page 81 and 82:
LA LINEA RECTA 75 Aunque (5) y {(3)
- Page 83 and 84:
en donde, LA LINEA RECTA 77 5 7 11
- Page 85 and 86:
LA LINEA RECTA 79 La longitud de la
- Page 87 and 88:
LA LINEA RECTA y de (9) y 5 (c), 5
- Page 89 and 90:
LA LINEA RECTA 83 y designemos por
- Page 91 and 92:
LA LINEA RECTA 85 tos de AC, del te
- Page 93 and 94:
LA LINEA RECTA 87 altura de B sobre
- Page 95 and 96:
LA LINEA RECTA 89 Como los puntos P
- Page 97 and 98:
LA LINEA RECTA en donde fe, la pend
- Page 99 and 100:
LA LINEA RECTA 93 Si ahora hacemos
- Page 101 and 102:
LA LINEA RECTA 95 8. Determinar el
- Page 103 and 104:
LA LINEA RECTA 97 10. Sin hallar su
- Page 105 and 106:
CAPITULO IV ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFE
- Page 107 and 108:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 101 P
- Page 109 and 110:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 103 1
- Page 111 and 112:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 105 E
- Page 113 and 114:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 107 L
- Page 115 and 116:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 109 5
- Page 117 and 118:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA Consi
- Page 119 and 120:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 113 E
- Page 121 and 122:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 115 e
- Page 123 and 124:
de d o n d e , ECUACION DE LA CIRCU
- Page 125 and 126:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 5. Di
- Page 127 and 128:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 121 o
- Page 129 and 130:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 123 S
- Page 131 and 132:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 125 4
- Page 133 and 134:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 127 L
- Page 135 and 136:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 129 2
- Page 137 and 138:
ECUACION DE LA CIRCUNFERENCIA 131 k
- Page 139 and 140:
CAPITULO Y TRANSFORMACION DE COORDE
- Page 141 and 142:
TRANSFORMACION DE COORDENADAS 135 n
- Page 143 and 144:
TRANSFORMACION DE COORDENADAS 137 C
- Page 145 and 146:
TRANSFORMACION DE COORDENADAS 139 1
- Page 147 and 148:
TRANSFORMACION DE COORDENADAS 141 E
- Page 149 and 150:
TRANSFORMACION DE COORDENADAS 143 5
- Page 151 and 152:
TRANSFORMACION DE COORDENADAS 145 s
- Page 153 and 154:
TRANSFORMACION DE COORDENADAS 147 E
- Page 155 and 156:
CAPITULO VI LA PARABOLA 53. Introdu
- Page 157 and 158:
LA PARABOLA 1 5 1 Recíprocamente ,
- Page 159 and 160:
LA PARABOLA 153 Un cada caso, la lo
- Page 161 and 162:
en donde las coordenadas del foco F
- Page 163 and 164:
LA PARABOLA 157 de la forma (4 ) re
- Page 165 and 166:
que pueden escribirse así, LA PARA
- Page 167 and 168:
LA PARABOLA 161 57. Ecuación de la
- Page 169 and 170:
LA PARABOLA 163 Resolviendo esta ec
- Page 171 and 172:
LA PARABOLA 165 Vimos en el Artícu
- Page 173 and 174:
LA PARABOLA 167 Solución. La funci
- Page 175 and 176:
LA PARABOLA 169 2p La pendiente de
- Page 177 and 178:
LA PARABOLA 171 E JE R C IC IO S. G
- Page 179 and 180:
C A PITU LO V il LA ELIPSE 60. Defi
- Page 181 and 182:
Elevando al cuadrado n u ev am en t
- Page 183 and 184:
LA ELIPSE 177 Consideremos ahora el
- Page 185 and 186:
LA ELIPSE 179 2. Desarrollar una di
- Page 187 and 188:
D e la ecuación (1 ) puede deducir
- Page 189 and 190:
LA ELIPSE 183 R ecíprocam ente, co
- Page 191 and 192:
LA ELIPSE 185 mayor y menor son de
- Page 193 and 194:
LA ELIPSE 187 Una im portante propi
- Page 195 and 196:
LA ELIPSE 189 4. Demostrar el sigui
- Page 197 and 198:
CA PITULO V III L A H IP E R B O L
- Page 199 and 200:
LA HIPERBOLA 193 en donde a es una
- Page 201 and 202:
LA HIPERBOLA 195 Si el centro de la
- Page 203 and 204:
LA HIPERBOLA 197 t/* 3. Deducir la
- Page 205 and 206:
LA HIPERBOLA 199 Por el teorema 9 d
- Page 207 and 208:
LA HIPERBOLA 201 Por el teorema 2 d
- Page 209 and 210:
LA HIPERBOLA 203 10. Discutir y tra
- Page 211 and 212:
LA HIPERBOLA 205 (3, 1 + V 13) y (3
- Page 213 and 214:
LA HIPERBOLA 207 12. Demostrar el t
- Page 215 and 216:
LA HIPERBOLA 209 9. Hallar el ángu
- Page 217 and 218:
PRIMER RESUMEN RELATIVO A LAS CÓNI
- Page 219 and 220:
dadas en el teorema 2 del Artículo
- Page 221 and 222:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 223 and 224:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 225 and 226:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 227 and 228:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 229 and 230:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 231 and 232:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 233 and 234:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 235 and 236:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 237 and 238:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 239 and 240:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 241 and 242:
ECUACION GENERAL DE SEGUNDO GRADO 2
- Page 243 and 244:
CAPITULO X COORDENADAS POLARES 79.
- Page 245 and 246:
COORDENADAS POLARES 239 A tal par l
- Page 247 and 248:
COORDENADAS POLARES Considerem os p
- Page 249 and 250:
COORDENADAS POLARES 243 EJERCICIOS.
- Page 251 and 252:
COORDENADAS POLARES 245 2. Sim etr
- Page 253 and 254:
COORDENADAS POLARES 247 3. Extensi
- Page 255 and 256:
COORDENADAS POLARES 249 de donde, p
- Page 257 and 258:
COORDENADAS POLARES 25 1 84. Fórm
- Page 259 and 260:
COORDENADAS POLARES 253 22. Demostr
- Page 261 and 262:
COORDENADAS POLARES 255 Los casos e
- Page 263 and 264:
COORDENADAS POLARES 257 las perpend
- Page 265 and 266:
COORDENADAS POLARES 259 centro C es
- Page 267 and 268:
COORDENADAS POLARES 261 del centro
- Page 269 and 270:
COORDENADAS POLARES 263 EJERCICIOS.
- Page 271 and 272:
CAPITULO X I ECUACIONES PARAMETRICA
- Page 273 and 274:
ECUACIONES PARAMETRICAS 267 Ejemplo
- Page 275 and 276:
ECUACIONES PARAMETRICAS 269 EJERCIC
- Page 277 and 278:
ECUACIONES PARAMETRICAS 271 instant
- Page 279 and 280:
ECUACIONES PARAMETRICAS 273 geom é
- Page 281 and 282:
ECUACIONES PARAMETRICAS 275 Una epi
- Page 283 and 284:
ECUACIONES PARAMETRICAS 277 en dond
- Page 285 and 286:
ECUACIONES PARAMETRICAS 279 8. Una
- Page 287 and 288:
ECUACIONES PARAMETRICAS 281 Como m3
- Page 289 and 290:
ECUACIONES PARAME TRICAS 283 EJERCI
- Page 291 and 292:
CAPITULO X II CURVAS PLANAS DE GRAD
- Page 293 and 294:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 287
- Page 295 and 296:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 289
- Page 297 and 298:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 291
- Page 299 and 300:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 293
- Page 301 and 302:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 295
- Page 303 and 304:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 297
- Page 305 and 306:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 299
- Page 307 and 308:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 301
- Page 309 and 310:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 303
- Page 311 and 312:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 305
- Page 313 and 314:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 307
- Page 315 and 316:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 309
- Page 317 and 318:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR Las
- Page 319 and 320:
CURVAS PLANAS DE GRADO SUPERIOR 313
- Page 321:
GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 324 and 325:
318 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 326 and 327:
320 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 328 and 329:
322 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 330 and 331:
324 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 332 and 333:
326 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 334 and 335:
328 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 336 and 337:
330 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 338 and 339:
332 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 340 and 341:
334 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 342 and 343:
336 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 344 and 345: 338 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 346 and 347: 340 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 348 and 349: 342 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 350 and 351: 344 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 352 and 353: 346 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 354 and 355: 348 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 356 and 357: 350 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 358 and 359: 352 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 360 and 361: 354 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 362 and 363: 356 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 364 and 365: 358 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 366 and 367: 360 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 368 and 369: 3 62 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACI
- Page 370 and 371: 364 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 372 and 373: 366 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 374 and 375: 368 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 376 and 377: 370 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 378 and 379: 372 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 380 and 381: 374 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 382 and 383: 376 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 384 and 385: 378 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 386 and 387: 380 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 388 and 389: 382 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 390 and 391: 384 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 392 and 393: 386 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 396 and 397: 390 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 398 and 399: 392 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 400 and 401: 394 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 402 and 403: 396 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 404 and 405: 398 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 406 and 407: 400 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 408 and 409: 402 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 410 and 411: 404 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 412 and 413: 406 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 414 and 415: 408 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 416 and 417: 410 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 418 and 419: 412 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 420 and 421: 414 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 422 and 423: 416 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 424 and 425: 418 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 426 and 427: 420 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 428 and 429: 422 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 430 and 431: 424 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 432 and 433: 426 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 434 and 435: 428 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 436 and 437: 430 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 438 and 439: 432 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 440 and 441: 434 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 442 and 443: 436 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 444 and 445:
438 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 446 and 447:
C A PITU LO X V II CURVAS EN EL ESP
- Page 448 and 449:
442 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 450 and 451:
444 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 452 and 453:
446 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 454 and 455:
448 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 456 and 457:
450 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 458 and 459:
452 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 460 and 461:
454 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 462 and 463:
APENDICE I LISTA DE REFERENCIA DE F
- Page 464 and 465:
458 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA 5. Determin
- Page 466 and 467:
460 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA en las figu
- Page 468 and 469:
462 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA 6. 8. Fórm
- Page 470 and 471:
464 APENDICE II A. L ogaritmos com
- Page 472 and 473:
466 APENDICE II B. F u n c io n es
- Page 474 and 475:
468 APENDICE II C. V alores de
- Page 476 and 477:
470 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA PLANA 16. (
- Page 478 and 479:
472 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA PLANA Grupo
- Page 480 and 481:
474 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA PLANA 14. -
- Page 482 and 483:
476 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA PLANA Grupo
- Page 484 and 485:
478 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA PLANA Grupo
- Page 486 and 487:
480 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA PLANA 5. 7x
- Page 488 and 489:
482 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA PLANA 25. r
- Page 490 and 491:
484 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 492 and 493:
486 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO
- Page 494:
488 GEOMETRIA ANALITICA DEL ESPACIO